Introduction to TPU Filament: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on TPU filament, a versatile and increasingly popular material in the world of 3D printing. With its unique properties, TPU filament has opened up new possibilities for creators, designers, and engineers alike. In this guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of TPU filament, discussing its definition, characteristics, types, and various applications.
We will also provide valuable tips and tricks for successfully printing with TPU filament and explore the key differences between TPU and other 3D printing materials. Whether you’re new to 3D printing or a seasoned professional, this guide aims to provide you with a wealth of knowledge about TPU filament and its potential uses. So, let’s embark on this exciting journey together and discover the true potential of TPU filament in the realm of 3D printing.
What is TPU Filament?
A variety of materials have arisen to fulfill the varying needs of designers and engineers as the field of 3D printing continues to develop. TPU filament is one such material, a flexible and adaptable choice that has revolutionized the potential of 3D printing projects. This section will give you an introduction to TPU filament by going through its definition, traits, and several market varieties. You will be better able to utilize TPU filament’s potential in your 3D printing projects if you comprehend its basic characteristics. So let’s dive in and learn more about the special qualities and uses of this fascinating substance.
Definition and characteristics
Thermoplastic polyurethane, or TPU filament, is a flexible and versatile material used in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing. With its unique combination of elasticity, strength, and durability, TPU filament has become increasingly popular for various applications.
TPU filament is known for its rubber-like properties, making it an ideal choice for printing flexible and functional objects. Additionally, it offers excellent resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and wear, ensuring the longevity of printed parts.
Types of TPU filament
There are several types of TPU filament available in the market, each with its specific characteristics and properties. Some common types include:
- Standard TPU: This is the most common form of TPU filament, offering a good balance of flexibility, strength, and ease of printing. It’s suitable for a wide range of applications, from phone cases to wearable items.
- Soft TPU: With a lower hardness rating than standard TPU, soft TPU provides increased flexibility and softness. This makes it perfect for projects that require extra comfort or flexibility, such as shoe insoles or custom-fit earbuds.
- High-strength TPU: This type of TPU filament is designed for heavy-duty applications, featuring improved tensile strength and resistance to wear. It’s ideal for parts that must withstand significant stress or strain, like protective gear or mechanical components.
In conclusion, TPU filament is a versatile material with unique characteristics that make it suitable for a wide range of 3D printing applications. By understanding the different types of TPU filament, you can choose the best option for your specific project needs.

Properties of TPU Filament
As you venture into the world of 3D printing, selecting the right material for your project is crucial. TPU filament, with its distinct set of properties, has emerged as a popular choice for various applications. In this section, we will delve into the key properties of TPU filament, including its flexibility, elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability. Understanding these properties will enable you to make informed decisions when choosing materials for your 3D printing projects and unlock the full potential of TPU filament. So, let’s explore the remarkable properties that make this material stand out among other 3D printing materials.
Flexibility and elasticity
This material is notable for its remarkable flexibility and elasticity. It can be twisted and stretched without breaking or losing its shape, unlike hard materials like PLA or ABS. This makes it ideal for making goods that need to be highly flexible, such as wearables, gaskets, or protective cases. Additionally, the material’s capacity to recover to its initial shape after stretching or deformation enables the printed parts to exhibit excellent shock absorption and impact resistance.
Chemical resistance
This material’s outstanding resistance to a variety of chemicals, such as oils, greases, and other solvents, is another notable quality. Because of this, it can be used in situations where the parts may need to survive strong chemicals or extreme weather. For instance, seals and gaskets manufactured of this material can act as strong barriers against chemical penetration and guarantee the durability of the components they are protecting.
Durability and abrasion resistance
The substance is renowned for its durability and resilience to wear and tear in addition to its adaptability and chemical resistance. It can survive frequent usage and exposure to harsh materials without significantly deteriorating its characteristics or appearance. This makes it the perfect material to use when making elements like gears, belts, and wheels that suffer constant friction. The material’s inherent hardness also extends the useful life and aesthetic appeal of the printed goods.
In conclusion, the material is a desirable option for a variety of 3D printing applications due to its flexibility, elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability. You can better use this amazing material to produce durable and useful printed parts by being aware of these characteristics.
TPU Filament and FDM 3D Printing
The combination of TPU material and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing technology has opened up new opportunities for creating flexible and durable objects. In this section, we will explore how TPU material interacts with FDM printers and discuss some of the common challenges and solutions associated with using this material. By understanding these aspects, you can optimize your 3D printing process and achieve better results with TPU material. Let’s dive in and discover the intricacies of working with this unique material in FDM 3D printing.
How TPU material works with FDM printers
FDM 3D printers work by melting a thermoplastic material, such as TPU, and depositing it layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. Due to its flexibility and elasticity, TPU material behaves differently than more rigid materials like PLA or ABS when used in FDM printers. The material’s softness can lead to challenges during the printing process, such as extruder jams or poor adhesion between layers. However, with proper printer settings and adjustments, it is possible to print high-quality objects with TPU material using FDM technology.
Common challenges and solutions when using TPU material
When working with TPU material, there are several challenges that you may encounter. Some of the most common issues and their respective solutions include:
Extruder jams
TPU material’s softness can cause jams in the extruder, leading to inconsistent extrusion or print failure. To overcome this, use a direct drive extruder or install a filament guide to ensure a smooth and consistent filament path.
Poor adhesion between layers
TPU material’s flexibility can result in weak layer bonding, which affects the object’s strength and durability. Increasing the extruder temperature or adjusting the print speed can help improve layer adhesion.
Stringing and oozing
Due to its elasticity, TPU material is prone to stringing and oozing during the printing process. To minimize this issue, fine-tune your retraction settings and experiment with different print speeds.
Bed adhesion
TPU material can sometimes struggle to adhere to the print bed, leading to warping or detachment during the printing process. To improve bed adhesion, use a heated bed, apply adhesion aids like blue painter’s tape, glue stick, or hairspray, and ensure the bed is leveled correctly.
Overheating
TPU material is sensitive to high temperatures, which can cause deformation or melting of the printed object. To prevent overheating, monitor and adjust the printing temperature as needed, and ensure proper cooling using a cooling fan or other cooling mechanisms.
Infill and support structure issues
Due to its flexibility, TPU material can sometimes cause issues with the infill and support structures, leading to weak or collapsed areas in the printed object. To overcome this, experiment with different infill patterns and densities, and adjust support settings to ensure proper support for overhangs and bridges.
Difficulty in removing supports
When printing with TPU material, removing support structures can be challenging due to the material’s flexibility and toughness. To address this issue, use a support material that dissolves in water, such as PVA, or design your object with minimal or easily removable supports.
By addressing these challenges and making the necessary adjustments, you can successfully print high-quality, flexible objects using TPU material with FDM 3D printers.
Printer Settings for TPU Filament
To achieve optimal results when printing with TPU material, it is essential to understand and adjust your printer settings accordingly. In this section, we will discuss the recommended printer settings for TPU material, covering extruder temperature, bed temperature, print speed, and retraction settings. By fine-tuning these parameters, you can enhance the print quality, reduce common issues, and create impressive, functional objects. Let’s explore the ideal printer settings for working with TPU material in FDM 3D printing.
Extruder temperature
The extruder temperature plays a crucial role in achieving successful prints with TPU material. The recommended temperature range for TPU material typically lies between 210°C and 250°C. However, the optimal temperature may vary depending on the specific TPU material brand and type. To find the best temperature for your TPU material, start with the manufacturer’s recommendation and gradually make adjustments based on your print results.
Bed temperature
To ensure proper adhesion of TPU material to the print bed, it is essential to set the bed temperature appropriately. A heated bed is recommended for TPU material, with a temperature range between 50°C and 80°C. As with the extruder temperature, the optimal bed temperature may vary depending on the specific TPU material, so experiment within this range and adjust based on your print results.
Print speed
Due to the flexible nature of TPU material, printing at a slower speed is often necessary to achieve better print quality and minimize issues like stringing or oozing. A print speed of 20-30mm/s is generally recommended for TPU material, although you may need to experiment to find the ideal speed for your specific printer and TPU material type.
Retraction settings
Retraction settings play a vital role in reducing stringing and oozing when printing with TPU material. Since TPU material is more flexible and elastic, it may require different retraction settings compared to rigid materials like PLA or ABS. Start by decreasing the retraction distance and increasing the retraction speed, and experiment with these settings until you achieve the desired results.
By understanding and adjusting the printer settings for TPU material, you can significantly improve your print quality, minimize common issues, and achieve successful prints with this flexible and versatile material in FDM 3D printing.
Tips for Successful TPU Filament Printing
Achieving successful prints with TPU material requires not only the right printer settings but also proper handling and techniques throughout the entire printing process. In this section, we will share valuable tips for successful TPU material printing, covering proper storage and handling, adhesion and bed preparation, and post-processing techniques. By following these tips, you can enhance your 3D printing experience with TPU material and create high-quality, flexible objects. Let’s dive in and explore these essential tips for successful TPU material printing.
Proper storage and handling
To ensure optimal print quality with TPU material, it is essential to store and handle the material correctly. Due to its hygroscopic nature, TPU material can absorb moisture from the air, which can negatively impact the printing process. Store your TPU material in a cool, dry place, preferably in a sealed container with desiccants. Before printing, check the material for signs of moisture and dry it if necessary using a filament dryer or a low-temperature oven.
Adhesion and bed preparation
Ensuring proper adhesion between the TPU material and the print bed is crucial for successful printing. As discussed earlier, using a heated bed and setting the appropriate temperature can significantly improve adhesion. Additionally, use adhesion aids like blue painter’s tape, glue stick, or hairspray to help the material stick to the bed. Clean the bed surface regularly and ensure that it is leveled correctly to further enhance bed adhesion.
Post-processing techniques
Post-processing TPU material can be challenging due to its flexibility and toughness. However, there are a few techniques you can use to achieve a clean and polished finish:
- Trimming and cutting: Use sharp, precision tools like hobby knives or scissors to remove excess material, such as strings or support structures, from your printed object.
- Sanding: Although sanding TPU material can be difficult, it is possible with patience and the right tools. Use fine-grit sandpaper or abrasive pads and apply gentle pressure to avoid damaging the object.
- Heat treatment: In some cases, using a heat gun or a hairdryer can help remove minor imperfections, such as strings or blobs, by slightly melting the material.
By following these tips for successful TPU material printing, you can improve your printing experience, minimize common issues, and create high-quality, functional objects with this versatile material.
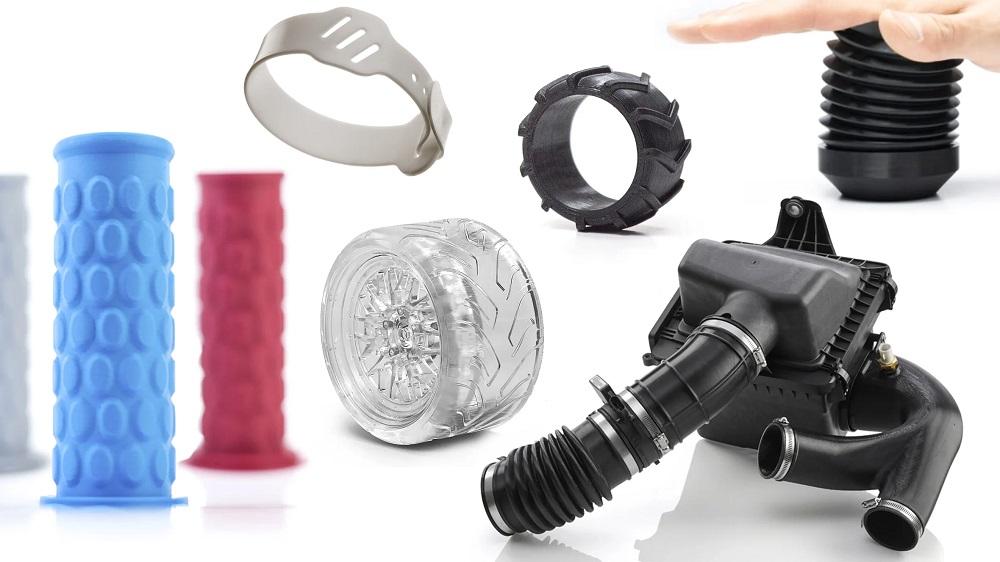
Popular Applications of TPU Filament
TPU material, with its unique combination of flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance, has found its way into numerous applications across various industries. In this section, we will explore some popular applications of TPU material in FDM 3D printing, including wearable and flexible items, gaskets and seals, protective cases and covers, and customized grips and handles. By understanding the potential uses of this versatile material, you can unleash your creativity and find innovative ways to incorporate it into your projects. Let’s dive into the exciting world of TPU material applications.
Wearable and flexible items
TPU material is ideal for creating wearable and flexible items, thanks to its soft and comfortable feel. For instance, TPU material has been used to create custom-fit athletic mouthguards, providing athletes with optimal protection and comfort. Similarly, TPU material can be used to print flexible wristbands or watch straps, offering a comfortable and personalized fit for the wearer.
Gaskets and seals
Due to its excellent chemical resistance and ability to maintain its shape under pressure, TPU material is perfect for creating gaskets and seals. A real-world example of TPU material in this application is the manufacturing of custom automotive gaskets, ensuring a proper seal and preventing leaks in various vehicle systems.
Protective cases and covers
The durability and shock-absorbing properties of TPU material make it an excellent choice for protective cases and covers. One common example is the creation of custom smartphone cases, which provide a snug fit and protect the device from everyday wear and tear, as well as accidental drops.
Customized grips and handles
TPU material’s slip-resistant and comfortable-to-touch surface makes it an ideal material for creating customized grips and handles for various tools and equipment. For example, TPU material can be used to create personalized bicycle handlebar grips, offering improved comfort and control for cyclists.
Medical devices and prosthetics
TPU material is well-suited for medical applications due to its biocompatibility, flexibility, and durability. It is used to create custom orthotics and prosthetics, such as flexible socket liners for prosthetic limbs, providing a comfortable fit and improved mobility for patients.
Industrial components
The toughness and chemical resistance of TPU material makes it an excellent choice for various industrial components. For example, TPU material is used to create flexible couplings and belts in machinery, reducing vibrations and noise while ensuring reliable performance.
Footwear and apparel
TPU material’s flexibility, durability, and comfort have made it a popular choice in the footwear and apparel industry. It is used to create custom insoles for shoes, offering improved support and cushioning for users. TPU material is also used in the production of flexible, waterproof clothing, such as rain jackets and outdoor gear.
Automotive and aerospace parts
The automotive and aerospace industries have embraced TPU material for its lightweight, strong, and resistant properties. One example is the use of TPU material to create flexible wire harness covers, providing protection and organization for electrical systems in vehicles and aircraft.
Robotics and soft actuators
In the field of robotics, TPU material has been employed to create soft actuators and flexible joints, allowing for smoother and more natural movements. TPU material can also be used to create soft robotic grippers, enabling the delicate handling of fragile objects.
These popular applications of TPU material showcase its versatility and potential in FDM 3D printing. By leveraging the unique properties of TPU material, you can create an array of functional and innovative items across various industries and applications.
TPU Filament Safety and Environmental Considerations
When working with TPU material, it’s important to understand the safety and environmental considerations that come with using this versatile filament. In this section, we will cover safe handling and disposal practices, health and safety precautions, the environmental impact of TPU material, and ….. By being aware of these considerations, you can ensure a safe and responsible experience while using TPU material in your 3D printing projects.
Safe handling and disposal
Handling TPU material properly is crucial for maintaining safety in your workspace. Always wear gloves when handling TPU material to prevent direct contact with the skin. Store TPU material in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain its quality. When disposing of TPU material, consult your local waste management guidelines, as some areas may have specific rules for disposing of plastics or chemicals.
Health and safety precautions
Although TPU material is generally safe to use, it is important to take health and safety precautions when 3D printing with this material. Ensure proper ventilation in your workspace to minimize the risk of inhaling any fumes produced during the printing process. Avoid touching the extruder nozzle during printing, as it can reach high temperatures and cause burns. Keep TPU material out of reach of children and pets to avoid accidental ingestion.
Environmental impact
Like any plastic material, TPU material has an environmental impact. The production of TPU material requires energy and resources, and it may contribute to waste when not disposed of properly. To minimize the environmental impact of TPU material, consider using recycled or eco-friendly TPU material options when available. Additionally, responsibly manage any waste by recycling or disposing of TPU material according to local guidelines.
Fire safety
While TPU material is not highly flammable, it can still pose a fire risk if exposed to high temperatures or open flames. Ensure your 3D printer and workspace comply with fire safety guidelines, and have a fire extinguisher readily available. Always monitor your 3D printer during operation to prevent any potential fire hazards.
Electrical safety
Ensure that you connect your 3D printer to a properly grounded electrical outlet to avoid electrical hazards, as with any electronic device. Regularly inspect the power cable and connections for signs of wear or damage. Avoid using extension cords or power strips, as they may not provide adequate electrical safety.
Material recycling
To minimize waste and reduce the environmental impact of TPU material, consider recycling any leftover or used TPU material. Many recycling facilities accept TPU material, and some 3D printing companies offer recycling programs for their customers. By recycling TPU material, you contribute to a circular economy and reduce the overall environmental impact.
Responsible sourcing
Consider purchasing TPU material from manufacturers that follow responsible sourcing practices and prioritize sustainability. This may include using recycled materials, reducing energy consumption during production, and minimizing waste in packaging. By supporting these manufacturers, you can help promote environmentally friendly practices in the 3D printing industry.
Workplace ergonomics
When working with 3D printers and TPU material for extended periods, it’s important to maintain proper ergonomics in your workspace. This includes ensuring comfortable seating, proper lighting, and maintaining good posture during work. By following ergonomic guidelines, you can reduce the risk of injury and promote overall health and well-being.
By being aware of these safety and environmental considerations, you can use TPU material in a responsible and eco-friendly manner, ensuring a safe and enjoyable 3D printing experience.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have discussed various aspects of TPU filament, including its definition, properties, applications, and safety and environmental considerations. By understanding these aspects, you can make informed decisions when using TPU material in your FDM 3D printing projects.
Key takeaways
- TPU filament is a versatile and flexible material that offers unique properties, such as flexibility, elasticity, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Proper printer settings, including extruder temperature, bed temperature, print speed, and retraction settings, are essential for successful TPU printing.
- TPU filament has a wide range of applications, from wearable and flexible items to gaskets, seals, protective cases, and customized grips and handles.
- It is important to follow safety and environmental guidelines when working with TPU material, including proper handling and disposal, health and safety precautions, and considering the material’s environmental impact.
Recommended actions
- When using TPU filament, ensure that you have the correct printer settings and follow best practices to avoid common challenges associated with TPU printing.
- Consider using TPU material in innovative applications, such as wearables, flexible electronics, and customized products.
- Always follow safety precautions and proper handling techniques to minimize risks and protect your health and the environment.
- Support sustainable practices in the 3D printing industry by purchasing TPU material from responsible manufacturers, recycling leftover material, and minimizing waste.
By following these recommendations, you can fully leverage the potential of TPU filament in your FDM 3D printing projects while ensuring a safe, responsible, and environmentally conscious experience.
How to design 3D models specifically for TPU material?
Tips on designing 3D models that take advantage of TPU’s unique properties, such as flexibility, elasticity, and durability. By following these steps, you can optimize your 3D models for TPU material and utilize its unique properties.
- Understand TPU material properties
Familiarize yourself with the unique properties of TPU, such as its flexibility, elasticity, and durability, and consider how they can be incorporated into your design.
- Design for flexibility and elasticity
TPU is best suited for designs that require flexibility or elasticity, such as phone cases, handles, or gaskets. Consider using filleted edges, rounded corners, or curved surfaces to optimize for these properties.
- Ensure proper wall thickness
TPU is a flexible material, and thin walls can easily deform or collapse during the printing process. Design your model with a minimum recommended wall thickness of 0.8mm to ensure structural integrity.
- Use support structures selectively
In general, TPU prints well without support structures. However, for complex geometries, adding support structures can help prevent deformation or sagging during the printing process
- Consider print orientation
The orientation of your 3D model during printing can impact the final strength and flexibility of the printed part. Experiment with different orientations to find the best balance of strength and flexibility for your design.
- Test and iterate
Before printing your final design, it is essential to perform several test prints and iterate as necessary to ensure that your design works as intended.
FAQs
TPU filament is a type of flexible and elastic thermoplastic polymer material commonly used in 3D printing.
TPU filament is highly flexible, durable, and abrasion-resistant, making it ideal for printing items like phone cases, gaskets, and seals.
Recommended settings for TPU filament include an extruder temperature of 220-240°C, bed temperature of 60-80°C, print speed of 20-40mm/s, and retraction settings turned off.
TPU filament should be stored in a dry, cool, and dark environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can negatively impact print quality.
Common challenges when printing with TPU filament include issues with bed adhesion, stringing, oozing, and deformation due to improper settings or handling.
Yes, TPU filament can be recycled, but the process can be difficult due to the material’s flexibility and elasticity. Some recycling facilities may not accept TPU for this reason.
Yes, TPU filament is generally safe to handle, but as with any 3D printing material, it is essential to follow proper handling and safety precautions to avoid injury.