Quality Control and assurance for Additive Manufacturing – What You Need To Know? How does It work? Why Is It Important? Where Do I Start?
introduction
The field of Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, has brought a revolutionary change. The product design, development, and manufacturing process has been transformed. The growth of this field is rapid, and it has brought a significant impact on traditional manufacturing methods. Companies and individuals can now produce complex and customized products more efficiently and cost-effectively by utilizing AM. This has opened up new possibilities and opportunities for innovation and creativity. It has opened up new opportunities in various industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer goods. It has enabled the creation of complex and intricate parts and products that were previously difficult or impossible to produce.
Quality Control and Assurance (QCA) is an essential aspect of AM. It ensures the end product meets the desired specifications, performance, and customer requirements. Consistent and accurate quality is crucial in AM. It must be maintained throughout the entire production process, from design to final inspection. Quality control can result in faulty parts, leading to costly rework, delays, and decreased customer satisfaction. For the success and growth of any business that relies on Additive Manufacturing (AM), it’s crucial to implement an effective Quality Control and Assessment (QCA) system. This will ensure that the final products meet the required standards. An effective QCA system helps to ensure that the products manufactured using AM meet the required quality standards.
The growth of the metal additive manufacturing industry is being held back by inconsistencies in quality, process reliability, and speed, affecting the cost-effectiveness of new applications. This is even though the technologies involved in metal additive manufacturing hold tremendous promise.

A brief explanation of Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, creates objects layer by layer using computer-aided design (CAD) models. Traditional manufacturing techniques involve cutting or shaping materials from a larger block. On the other hand, 3D printing adds material in a precise and controlled way to create the final product. This enables the creation of complex shapes. These shapes were previously challenging or even impossible to produce with conventional methods.
Over time, 3D printing technology has advanced and expanded to encompass a range of materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Additionally, it includes various techniques such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS). The adaptability and versatility of 3D printing make it a popular choice for prototypes, small-scale production runs, and even mass production. Industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer goods rely on 3D printing technology.
Importance of Quality Control and Assurance in AM
We cannot overstate the importance of Quality Control and Assurance (QCA) in Additive Manufacturing (AM). It plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications, performance, and customer requirements. It is crucial to maintain consistent and accurate quality in AM throughout the production process, from design to final inspection. By implementing effective QCA systems, businesses can detect and correct any potential defects or inconsistencies in the product, reducing the risk of costly rework, delays, and customer dissatisfaction.
A robust QCA system can improve the reliability and performance of the final product. This is particularly important in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries, where even the tiniest defect in a component can have severe consequences. AM-based businesses must invest in quality control and assurance. This is not just a best practice but also a requirement for many industries.
Types of quality control for additive manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing (AM) can ensure the final product meets specific requirements, performance and client needs by using several Quality Control and Assurance (QCA) procedures. Let’s look at some of the most popular QCA approaches in AM:
In-Process Testing: It is critical to monitor and check the product at various stages of production to ensure it satisfies quality requirements.
Dimensional Inspection: This sort of quality control ensures that the dimensions of the product, such as length, width, height, and angles, are within tolerance limits.
Material Verification: Before employing a material for production, its qualities, such as density, tensile strength, and thermal conductivity, must be verified to ensure it fits the requirements for the intended application.
Visual Inspection: It is critical to visually evaluate the product’s surface polish, cracks, and other faults to ensure that it satisfies the necessary quality requirements.
Post-Process Inspection: Finally, it is critical to inspect the finished product after the manufacturing process to ensure it fulfills the specifications.
AM firms may ensure consistent and precise quality, reduce the chance of defects, and improve customer satisfaction by adopting these and other QCA procedures. Investing in quality control and assurance can also help a company create a reputation for providing high-quality products, leading to overall success and expansion.
In-Process Inspection for quality control for additive manufacturing
In Additive Manufacturing (AM), in-process inspection entails monitoring and inspecting the product at various phases of the manufacturing process. This sort of quality control assists in identifying any problems or deviations early on and making the required adjustments to guarantee that the final product satisfies the specified quality standards. In-process inspection can include, among other things, inspections for material characteristics, dimensional correctness, and surface polish. AM-based firms can reduce the risk of defects. They can achieve this by implementing in-process inspection. This improves the overall quality of their goods and boosts customer satisfaction.
Dimensional Inspection
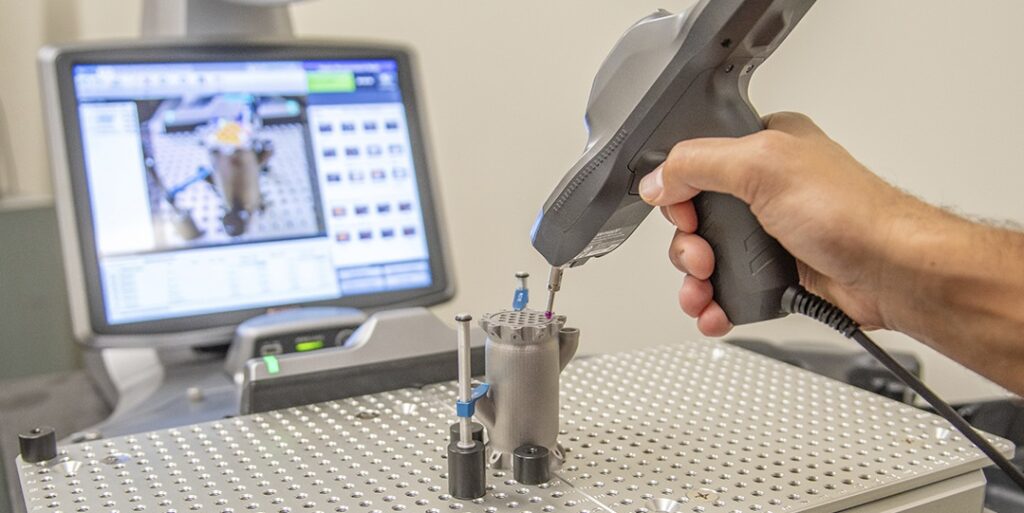
Dimensional inspection in AM focuses on ensuring that the product’s dimensions, such as length, breadth, height, and angles, satisfy the prescribed tolerance limits. This type of quality control is crucial for items with stringent dimensional constraints, such as those used in aircraft, medicine, and automobiles. Dimensional inspection can use several measuring tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). AM-based organizations can improve overall product quality and reduce the risk of product failure. They can achieve this by ensuring dimensional accuracy.
Material Verification for 3d print quality
In additive manufacturing, material verification checks the material’s qualities, such as density, tensile strength, and thermal conductivity, to confirm that it meets the required standards for the intended use. This type of quality control is necessary since the material’s qualities affect the overall performance and dependability of the product. Several testing procedures, including tensile testing, hardness testing, and thermal analysis, can help you accomplish material verification. AM-based firms can reduce the risk of product failure and improve overall product quality. They can do this by checking the material qualities.
Visual Inspection for quality control for additive manufacturing
In AM, visual inspection entails checking the product’s surface polish, cracks, and other faults to ensure that it satisfies the necessary quality requirements. To accomplish this quality control, trained inspectors employ several visual inspection tools, such as magnifying lenses, microscopes, and stereo microscopes. Visual inspection is especially critical for products that must meet cosmetic standards, such as those in the consumer goods industry. AM-based enterprises can ensure their goods have a high-quality surface finish and are free of defects by conducting a visual inspection. This contributes to customer satisfaction.
Post-Process Inspection
In AM, post-process inspection entails checking the final product to ensure that it satisfies the stated standards after the manufacturing process has been completed. This quality control is crucial for assuring overall product quality and might involve inspections for dimensional accuracy, material qualities, and surface polish, among other things. Several measuring and testing tools, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and tensile testers, can be used for post-process inspection. AM-based enterprises may ensure that their products meet the desired quality requirements and are defect-free by doing the post-process inspection, which contributes to customer happiness and overall product success.
Quality Control In Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, quality control ensures that consumers receive products free from defects and satisfy their requirements. It is possible to endanger customers if it is carried out improperly. For instance, the recent discovery of a flaw in Takata airbags led to the largest recall of automobiles in the annals of the automotive industry. The recall affected over 69 million airbag inflators and is costed many billions. The recall continued until the end of 2020.
Large-scale recalls like this can be avoided with proper quality control throughout manufacture. The following are examples of standard instruments used to help quality control:
Statistical process control (SPC) ensures product quality by monitoring and controlling many production indicators. It allows quality managers to spot issues and find solutions to them before items leave the facility.
Six Sigma relies on five fundamental concepts to guarantee that the end products are faultless and satisfy the client’s requirements.
When backed by lean technologies such as Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), 5S, and Kaizen, it is possible to eliminate the vast majority of problems, if not all.
Benefits of Implementing Quality Control and Assurance in AM
Integrating quality control and assurance (QC&A) into Additive Manufacturing (AM) provides various benefits that can improve the overall performance and success of AM-based organizations. Here are some of the primary advantages of integrating QC&A in AM:
Superior Product Quality: By using QC&A, firms can ensure that their products meet defined quality standards, resulting in a better final product. This reduces the possibility of product failure and increases customer satisfaction, resulting in more significant sales and revenue.
Incorporated QC&A can assist in discovering and resolving errors early in the manufacturing process, eliminating the need for further work and saving time and costs. This results in better efficiency and productivity, which leads to increased profitability.
More substantial Reputation: QC&A helps organizations establish a reputation for producing high-quality products. This is especially crucial for businesses in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive. This increases client trust and loyalty, increasing sales and revenue.
Implementing QC&A is critical for organizations operating in regulated industries such as medical and aerospace. It helps assure compliance with industry norms and standards. This reduces the danger of penalties and legal fees, resulting in higher profits.
Increased Innovation: Using Quality Control and Assurance (QC&A) provides critical insight into the manufacturing process and product performance. This information can then be used to drive continuous improvement and innovation. As a result, processes are improved, new products are developed, and competitiveness and profitability are raised.
Adopting quality control and assurance in Additive Manufacturing has various advantages. It can improve the overall performance and success of AM-based organizations. Businesses can improve their sales and revenue by reducing the chance of product failure. They can also increase customer happiness by ensuring their products meet quality standards.
Manufacturing QC benefits
Customers anticipate and insist on purchases of high-quality goods. When clients purchase products of sufficient quality, you will:
- Improve the level of consumer loyalty.
- Acquire a loyal customer base.
- Acquire new clients through word-of-mouth advertising.
- Keep your current position on the market or make it even stronger.
- Improve safety
- Reduce the risks of potential liability
- Make a positive contribution to the overall branding of your product.
Quality control measures reduce the risk of product recalls and protect customers from poorly constructed items. They also ensure that manufacturers are held to a high standard, increasing confidence in the products they produce. The expenses incurred as a result of these recalls can be significant.
Find out how you can assist your quality control system with TPM and avoid costly recalls simultaneously. Enhance the product’s quality, eliminate any faults, and boost your revenues.
Quality Assurance with Quality Control
The quality assurance process expedites manufacturing and ensures that the finished goods fulfill the quality criteria established by the firm. It guarantees that the procedures used to design, test, and create products will be carried out properly.
Quality assurance in manufacturing is crucial for successful operations. Approaches such as ISO 9001 help to manage and improve various aspects of manufacturing, including production processes and customer satisfaction.
- Obtaining the necessary raw resources
- The procurement of sub-assemblies and components from third parties
- Developing and utilizing different methods of inspection
- maintaining conformity with manufacturing procedures
- Taking action in response to flaws
Quality assurance might seem highly different depending on the company. ISO 9001 applies to companies of any size. It can be modified to meet virtually any requirement. Additive Manufacturing (AM) enables the creation of a long-lasting quality assurance program. This program guarantees the exceptional quality of all aspects of the product, from raw ingredients to inspection procedures. Nearly eradicating problems and faults from defective materials or components sourced from a third party. These actions have significantly improved the quality of products.
Quality Assurance in Additive Manufacturing
Recent years have seen a surge in the pace of research into quality control (QC) in AM. Mechanical and material elements applied to various fields have high practicality, reliability, and growth. This results in their widespread use in various industries. Hollister (2015) categorized numerous processes in a preliminary consideration of AM technology in QC to satisfy design requirements. He conducted research on a splint commonly used in the medical field. He documented his findings in the publication by Hollister et al. (2015). The image below displays five distinct processes that make up the design control process.
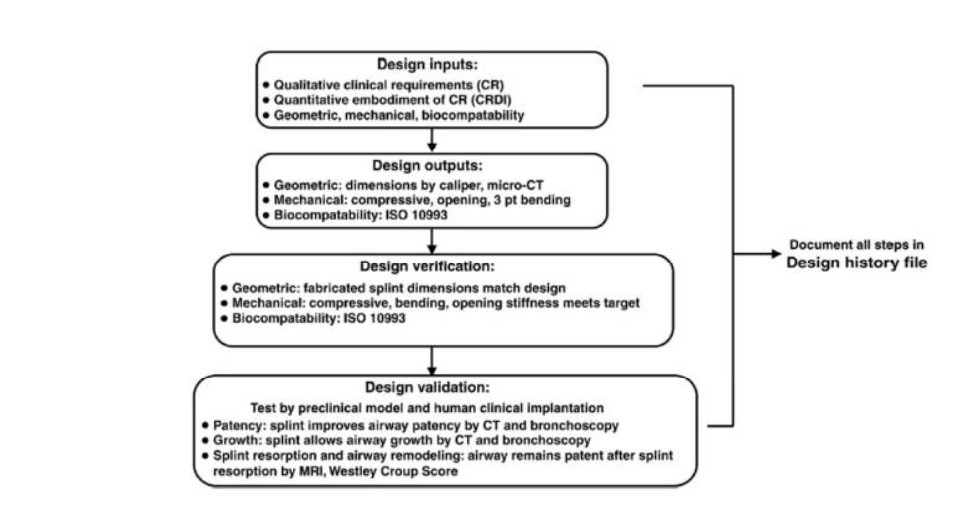
To design and model a part that meets all necessary mechanical and specific criteria, you must first complete a design input. This process requires considering factors such as laser power, speed, particle size, and more. The design team carries out tests as the second step in the design process. They measure the design input following standard operating procedures. These tests determine the splint’s compressive, bending, and opening stiffness by employing the destructive evaluation method. The design output is the result of these measurements.
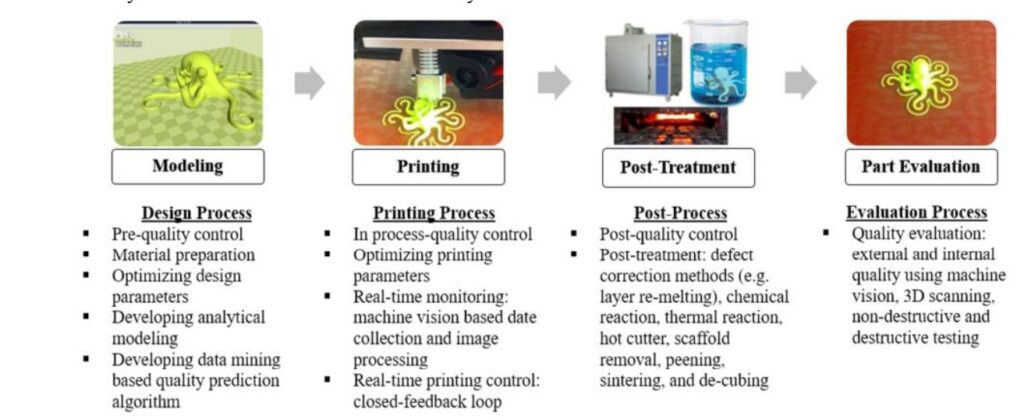
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Quality Control and Assurance in AM
Despite the numerous benefits of incorporating quality control and assurance (QC&A) into Additive Manufacturing (AM), there are also several challenges that businesses must overcome to ensure its successful implementation.
Challenges
- Lack of Standardization: AM is still a relatively new technology, and there are few widely-accepted standards for quality control and assurance in AM. This can make it difficult for businesses to implement QC&A and ensure their products conform to established quality standards.
- The complexity of AM Processes: The nature of AM, with its complex and intricate shapes and structures, can make it challenging to implement effective QC&A processes. This can lead to increased costs, longer lead times, and reduced competitiveness and profitability.
- Limited Availability of Testing Equipment: Specialized equipment is necessary for testing and evaluating the quality of parts produced through Additive Manufacturing (AM). This equipment, however, may not be readily available and affordable for small and medium-sized businesses, making it a challenge for them to use AM effectively. This can limit the ability of these businesses to implement effective QC&A processes.
solutions
- Adopting Industry Standards: Businesses can adopt existing industry standards, such as ISO 9001, to ensure their products conform to established quality standards.
- Investing in Testing Equipment: Businesses can invest in testing equipment and technologies, such as x-ray computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound, to evaluate the quality of their products. This will ensure the implementation of effective QC&A processes.
- Implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC involves collecting and analyzing data from the production process to identify trends and improve quality. This can help businesses identify and resolve quality issues earlier in production, reducing product failure risk.
- Partnering with Expert Service Providers: Businesses can partner with expert service providers, such as quality control and assurance consulting firms, to ensure the successful implementation of QC&A in AM. These providers can offer guidance, support, and best practices for implementing effective QC&A processes.
In conclusion, implementing quality control and assurance in AM presents several challenges. Still, businesses can overcome these challenges by adopting industry standards, investing in testing equipment, implementing statistical process control, and partnering with expert service providers. Doing so can ensure their products conform to established quality standards and improve their competitiveness and profitability.
conclusion
In conclusion, to ensure that the final product meets the desired quality standards, the Additive Manufacturing (AM) process must include quality control and assurance. Critical components of AM, Quality control and assurance, cannot be neglected. AM technology has come a long way, and its versatility and flexibility make it an attractive option for various industries. However, to fully reap the benefits of AM, businesses must implement effective QC&A processes. Overcoming the challenges in implementing QC&A in Additive Manufacturing (AM) requires adopting industry standards, investing in testing equipment, implementing statistical process control, and partnering with expert service providers. By taking these steps, companies can ensure that they are effectively addressing the challenges posed by QC&A in AM and are able to produce high-quality products with greater consistency and reliability. By doing so, businesses can ensure their products conform to established quality standards and improve their competitiveness and profitability.
key points
This blog post highlights the significance of quality control and assurance in Additive Manufacturing (AM), often referred to as 3D printing. We delve into the topic and explain why it is crucial in this field. We cover the types of QC&A that are crucial in AM, the benefits of implementing these processes, and the challenges and solutions involved. Through this post, we aim to provide an overview of the key points that businesses should keep in mind while incorporating QC&A into their AM production processes. By the end of this post, you will have a clear understanding of the importance of QC&A in AM and the steps you can take to ensure your products meet the desired quality standards.
- Additive Manufacturing (AM) builds objects layer by layer using a computer-aided design (CAD) model, adding material in a precise and controlled manner.
- The implementation of quality control and assurance (QC&A) is essential in AM to ensure the final product meets desired quality standards.
- To overcome the challenges of implementing QC&A in AM, follow industry standards, invest in testing equipment, implement statistical process control, and seek help from expert service providers. This will ensure a successful implementation of QC&A in the field of AM.
- By incorporating QC&A into the production process, businesses can ensure their products conform to established quality standards and improve competitiveness and profitability.
FAQ
In AM, quality control and assurance are critical to ensuring that the finished product satisfies the necessary quality requirements and is free of defects or inconsistencies.
In-process monitoring, post-process inspection, statistical process control, and material testing are all examples of QC&A in AM.
Improving product quality, reducing waste and rework, increasing competitiveness and profitability, and improving customer satisfaction are all advantages of integrating QC&A in AM.
The difficulties in implementing QC&A in AM include limited resources, a lack of industry standards, and the technology’s complexity.
Following established industry standards, investing in testing equipment, establishing statistical process control, and getting assistance from skilled service providers can help overcome these problems.







