Sheet Lamination Process: Revolutionizing 3D Printing
Introduction to Sheet Lamination Process
A 3D object is created by fusing layers of material together using the Sheet Lamination Process, an additive manufacturing technique. It varies from other 3D printing methods in that it uses material sheets rather than filaments or powders, a development that occurred in the early 1990s. The final result can be manufactured from a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, and metal. The method requires using a laser or adhesive to attach the layers.
Definition and a brief history of the process
In 1991, Michael Feygin received the first patent for the Sheet Lamination Process, often known as Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM). The process involves layering sheets of material, such as paper or plastic, on top of one another in the desired shape, using an adhesive. Then, the layers are laser-cut into the desired shape and bonded together to create the finished product. LOM was one of the first 3D printing technologies developed, and it has since been used to produce a range of items.
Overview of how it differs from other 3D printing technologies
The Sheet Lamination Process is economical and effective. It is better than other 3D printing methods. It can use a variety of materials. These include paper, plastic, and metal. This makes it a flexible technology. It is usable in various sectors. The technique also produces less trash due to the lack of support structures, making it a more environmentally responsible choice.
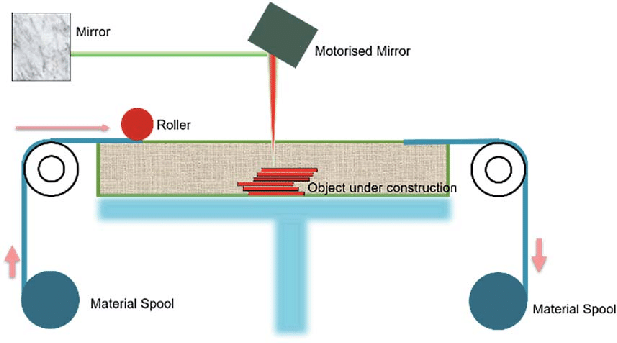
Types of Sheet Lamination Process
Sheet Lamination Process is an innovative additive manufacturing technology that has gained popularity due to its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness. This process involves the bonding of layers of materials, such as paper, plastic, and metal, to create a 3D object. There are various types of Sheet Lamination Processes, each with its own unique features and advantages. Let’s explore popular Sheet Lamination Processes. Examples are Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM), Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing (UAM). Understanding differences helps determine which suits the application.
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
Sheet Lamination Process is Laminated Object Manufacturing. It cuts sheets of material into shapes. The material is usually paper or plastic. It bonds them with adhesive. The laser or blade then cuts the layered sheets to shape, creating a 3D object. LOM offers low cost and fast production time, which makes it an ideal process for creating large, low-resolution objects.
Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing (UAM)
Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing is a Sheet Lamination Process that uses ultrasonic vibrations to bond layers of metal together. The process involves the use of a sonotrode, which generates high-frequency vibrations that create friction between the layers of metal, causing them to bond together. The aerospace and automotive industries popularly choose UAM for its ability to create complex metal parts with high precision.
The Working Principle of the Sheet Lamination Process
The Sheet Lamination Process produces intricate 3D structures. It uses a range of materials. It’s an additive manufacturing technology. Technology has grown in popularity. It’s because of its capacity. Its popularity has increased in recent years. Layers of material are fused together during the procedure to form a solid item. Although the Sheet Lamination Process comes in a variety of forms, its fundamental operation is the same. Detailed steps in sheet lamination operation and material function examined. Understanding sheet lamination basics aids in appreciating technology adaptability. Sheet lamination potential for numerous industries increased with basic comprehension.
The step-by-step process of how it works
Sheet Lamination Process involves the bonding of multiple layers of material to create a three-dimensional object. The process begins with the selection of suitable materials, which can include paper, plastic, or metal sheets. A laser or blade cutter cuts these materials into precise dimensions. Then, the surface of each layer receives an adhesive application. The layers bond together using the adhesive while being stacked. Pressure and heat activate the adhesive, binding the layers together. A trimming process removes excess material, and the finished 3D object is ready for use.
The role of materials used in sheet lamination
The choice of materials is a crucial aspect of the Sheet Lamination Process, as it directly affects the quality and properties of the finished object. The materials used must be flexible and easily bendable, yet strong enough to maintain their shape once bonded together. The thickness and composition of the sheets can also impact the final result. For instance, thin sheets can produce finer details, while thicker sheets can offer greater structural integrity. Additionally, the type of adhesive used is also important, as it should provide a strong, durable bond without adding too much weight or altering the properties of the material. By carefully selecting the materials and adhesive, manufacturers can produce 3D objects with the desired properties and characteristics.
Advantages of Sheet Lamination Process
Sheet Lamination Process is a revolutionary manufacturing technology that offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. From high accuracy and precision to low cost and fast production, this process has a lot to offer. Sheet Lamination Process is eco-friendly. It’s an alternative to traditional manufacturing. It’s sustainable and attractive for businesses. The process has advantages, such as high accuracy and precision. It’s also low-cost and fast. It offers customizable designs for various applications. By understanding these advantages, we can better appreciate the potential of the Sheet Lamination Process in various industries and applications.
High accuracy and precision in printing
The Sheet Lamination Process bonds material layers for accuracy and precision. It creates intricate designs and details. Specialized software and equipment allow precise control. This results in a high-quality finished product.
Low cost and fast production
One of the key advantages of the Sheet Lamination Process is its low cost and fast production. Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, Sheet Lamination Process can significantly reduce the cost of production by eliminating the need for expensive molds and tooling. Additionally, the process can be completed quickly, allowing for faster production times and shorter lead times.
Eco-friendly and sustainable
Sheet Lamination Process is also an eco-friendly and sustainable manufacturing process. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that produce a lot of waste, Sheet Lamination Process produces little to no waste. Additionally, the process consumes less energy, and renewable energy sources can power it, making it a more sustainable alternative to traditional manufacturing methods.
Customizable designs for various applications
Sheet Lamination Process allows for customizable designs for various applications. The process’s versatility in using a variety of materials and creating complex shapes and structures makes it applicable in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer goods. This allows for customized designs that meet specific requirements and needs, resulting in a more effective and efficient final product.
Limitations of Sheet Lamination Process
While Sheet Lamination Process offers many advantages over traditional manufacturing methods and other 3D printing technologies, it is not without its limitations. In this section, we will explore some of the key limitations of the Sheet Lamination Process, including the constraints on material choice and thickness, limited resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies, and the complexity of post-processing. Understanding these limitations can help designers and manufacturers make informed decisions about whether Sheet Lamination Process is the right technology for their specific needs and applications.
Constraints on material choice and thickness
One of the major limitations of the Sheet Lamination Process is the constraints on material choice and thickness. Unlike other 3D printing technologies, Sheet Lamination Process is limited to a narrow range of materials that can be used for printing. Additionally, the thickness of the materials used in the process must be within a certain range to ensure successful bonding and construction of the object.
Limited resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies
Another limitation of the Sheet Lamination Process is its limited resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies. While Sheet Lamination can produce high-quality objects, its resolution is lower than other technologies such as stereolithography or digital light processing. This can limit the level of detail and intricacy that can be achieved in the final product.
Complexity of post-processing
Sheet Lamination Process also presents challenges in post-processing. Because the finished product is made up of bonded layers of material, post-processing can be complex and time-consuming. Removing support structures and achieving a smooth finish can be difficult, requiring specialized equipment and expertise. This can increase the cost and time required for post-processing and finishing the final product.
Applications of Sheet Lamination Process
Applications of the Sheet Lamination Process are vast and diverse, thanks to its unique advantages and capabilities. This technology is commonly used in product design and prototyping to create accurate and functional prototypes of new products. Manufacturers also use it to produce complex parts like gears, bearings, and other mechanical components. The medical industry benefits from the Sheet Lamination Process by using it to create custom implants and prosthetics for patients. The aerospace industry also increasingly relies on the Sheet Lamination Process to create high-performance, lightweight components for aircraft and spacecraft. As the technology continues to evolve and improve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications for Sheet Lamination Process in the future.
Automotive and aerospace industries
Automotive and aerospace industries are among the primary areas where Sheet Lamination Process finds extensive application. The automotive industry utilizes sheet lamination to manufacture customized parts with enhanced strength and durability. This process can produce functional prototypes like gears and housings for testing in diverse environments. Similarly, the aerospace industry employs sheet lamination to manufacture complex and lightweight components such as turbine blades and ducting systems. The ability to print high-strength materials in complex geometries allows for the production of parts with improved performance characteristics. Additionally, the sheet lamination process provides these industries with the flexibility to customize designs and create small batches of parts economically, without the need for costly tooling.
Medical and dental fields
The sheet lamination process has found various applications in the medical and dental fields due to its ability to produce customized and intricate parts with high accuracy and precision. Sheet lamination processes allow for producing dental implants by printing biocompatible materials layer by layer based on the patient’s jaw structure. This method also facilitates the fabrication of prosthetics and orthotics, providing patients with better fitting and more functional devices. Moreover, manufacturers have utilized sheet lamination to produce surgical models and tools, leading to more efficient and effective surgical planning and procedures. The ability to produce parts with complex geometries and fine details has made sheet lamination a valuable technology in the medical and dental fields, with the potential for further advancements and applications.
Art and design
Because the sheet lamination process makes it simple to create intricate, high-quality models, it can be very useful in the fields of art and design. With the use of this technology, designers can rapidly and effectively construct precise prototypes of their designs so they can test and improve them. Sheet lamination enables designers and artists to create intricate models with various colors and textures, making it an excellent tool to bring their creations to life. Designers and artists use sheet lamination to create sculptures, unique jewelry, and architectural models, among other things. Sheet lamination is a useful tool for artists and designers to create original and creative works since it can produce intricate and highly detailed designs.
Future of Sheet Lamination Process
The sheet lamination process has come a long way since its introduction and continues to evolve. The future of this technology seems to be promising, especially with the development of new materials and the increasing demand for customization. One potential area of growth for sheet lamination is in the biomedical field, where it can be used to create custom implants and prosthetics. Another possible application is in the creation of functional prototypes and tooling for manufacturing processes. Additionally, advancements in software and automation are expected to make the process more efficient and accessible for a wider range of industries. Overall, the future of sheet lamination looks bright, and it will likely continue to be a valuable tool for manufacturing and design in the years to come.
Innovations and advancements in technology
The field of sheet lamination process has been significantly touched by technological innovations and improvements. Accuracy, speed, and customizability have all significantly improved with the advent of new materials and methods. Designers and engineers may now easily create complicated structures and patterns thanks to the usage of computer-aided design (CAD) and additive manufacturing. Automation and robotics integration has also improved productivity and decreased labor expenses. Additionally, the development of new biodegradable and sustainable materials has improved the environmental friendliness of the sheet lamination process. It is expected that other developments may result in even greater advancements in the field of sheet lamination process as technology continues to develop.
Potential for integration with other manufacturing processes
The potential for integrating sheet lamination technology with other manufacturing processes is vast. By combining sheet lamination with other 3D printing techniques, designers and engineers can produce complex parts with high accuracy and speed. Companies can use sheet lamination as a complementary process to traditional manufacturing methods, such as injection molding, to create prototypes or small production runs quickly and cost-effectively. Furthermore, the ability to produce laminated sheets of varying materials and thicknesses opens up opportunities for integrating sheet lamination into a wider range of manufacturing processes, such as electronics, textiles, and packaging. Manufacturers will likely continue to expand the integration of sheet lamination technology with other manufacturing processes as the technology evolves and new applications are discovered.
Conclusion
In conclusion, various fields, including automotive, aerospace, medical and dental, and art and design, have applied Sheet Lamination Process as a versatile and innovative additive manufacturing technique. Its potential for integration with other manufacturing processes makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to streamline their production processes. The advancements in technology and the continuous development of new materials have opened up new possibilities for the use of the Sheet Lamination Process. As a result, the future looks bright for this technique, and it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in the manufacturing industry. Despite some limitations, the benefits of the Sheet Lamination Process outweigh the challenges, and it is an exciting time for the technology.
Summary of the benefits and drawbacks of the sheet lamination process
The sheet lamination process has a number of advantages and disadvantages. The capacity to create complex geometries with exceptional accuracy and precision is one of the key benefits. The procedure also permits the use of a wide range of substances, such as metals, ceramics, and polymers. The fact that the materials and equipment needed for the procedure are reasonably inexpensive is another benefit.
The sheet lamination process is not without its flaws, though. The size of the parts that can be produced is one of the key restrictions, as the method is often best suited for smaller components. The application and curing of each layer separately make the process time-consuming as well. Additionally, the final product might be weaker than those made using other manufacturing techniques, making it less appropriate for use in high-stress situations.
When selecting a manufacturing process for a specific application, it is important to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the sheet lamination process.
Final thoughts on its impact on the future of manufacturing and 3D printing.
In conclusion, the sheet lamination process has the potential to transform the manufacturing and 3D printing industries by offering a practical and affordable means of production. It is a flexible solution for numerous industries because it can produce parts with a variety of materials and shapes. Its attractiveness is also boosted by the fact that the method is non-toxic and safe for the environment. It also has several disadvantages, like restrictions on part size and mechanical attributes. But as long as technology develops, these shortcomings will probably be fixed, and sheet lamination’s advantages will only get better. Overall, 3D printing and manufacturing have a lot of potential thanks to the sheet lamination process.
How to optimize the sheet lamination process for time and cost efficiency?
- Evaluate your current process
Take a close look at your current sheet lamination process and identify any areas where you may be experiencing inefficiencies. This could include things like excessive material waste, lengthy setup times, or inconsistent print quality.
- Set clear goals
Define clear goals for what you want to achieve in terms of time and cost efficiency. This will help you stay focused on the most important areas for improvement.
- Consider automation
Look for ways to automate your sheet lamination process, such as using robots for material handling or implementing software to streamline job setup and scheduling.
- Optimize material usage
Reduce material waste by optimizing the nesting of parts and minimizing the amount of support material used.
- Standardize your process
Establish a standardized process that includes clear work instructions and quality control measures. This will help ensure consistency and efficiency across all jobs.
- Invest in training
Ensure your staff is properly trained in the sheet lamination process, including best practices for optimizing time and cost efficiency.
- Monitor and measure performance
Track your progress toward your goals and regularly measure key performance indicators, such as cycle time and scrap rate, to ensure you’re on track.
FAQs
The sheet lamination process offers several advantages, including low cost, easy setup, and the ability to print large and complex parts.
While the sheet lamination process is capable of producing parts with good accuracy and quality, it may not be the best option for high-volume industrial production due to its relatively slow printing speed.
The sheet lamination process has some advantages over other 3D printing technologies, such as its low cost and the ability to print large parts. However, it may not be as precise or detailed as some other technologies.
Yes, the sheet lamination process is compatible with a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, and metal sheets.
Several factors can affect the quality and efficiency of the sheet lamination process, such as the type and quality of materials used, the thickness of the sheets, the temperature and humidity of the environment, and the accuracy and calibration of the printer.
Yes, the sheet lamination process can be a good option for prototyping due to its low cost and ease of use. However, it may not be as precise or detailed as some other 3D printing technologies.