Introduction
In this post, we will be examining the properties and performance of sheet lamination materials. Sheet lamination is a form of additive manufacturing that bonds together layers of material to produce a final product. Industries like packaging, printing, and woodworking have employed this technique for many years. However, with the emergence of 3D printing and other additive manufacturing technologies, sheet lamination has garnered renewed interest.
In sheet lamination, thin material layers are stacked and bonded using heat, pressure, or adhesives. This method is cheaper, faster, and more precise than other additive manufacturing methods. It may be utilized with a variety of materials, including paper, plastics, and metals.
The performance and characteristics of sheet lamination materials will be the main topics of this essay. We’ll cover sheet lamination materials and their properties. Each material has its strengths, flexibility, and thermal characteristics. Material properties impact cutting, bonding, and finishing. We’ll offer advice to improve material performance for specific uses.
Definition of sheet lamination and its role in additive manufacturing
Sheet lamination involves layering thin sheets of material to create objects. It’s a form of additive manufacturing. Bonding is used to connect the sheets. The end result is a final object. This process is widely used in various industries, such as packaging, woodworking, and printing.
In sheet lamination, materials are bonded together using a variety of techniques, including heat, pressure, and adhesives. This allows for the creation of objects with high accuracy and detail, making it a popular choice for producing small, intricate parts.
Sheet lamination plays a crucial role in additive manufacturing as it offers several advantages over other techniques. For instance, it is a cost-effective method that requires less time and resources than traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, it allows for the creation of complex shapes and structures that would be difficult to achieve using other manufacturing techniques.
Sheet lamination is flexible and effective in making small and complex objects. It bonds materials together, offering several benefits. Manufacturers in various industries find it attractive.
Importance of material properties and performance in sheet lamination processes
The properties and performance of materials used in sheet lamination are crucial factors in the success of the manufacturing process. These properties can impact the final product’s strength, flexibility, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. Therefore, understanding the importance of material properties is essential for optimizing sheet lamination processes.
One important property to consider is the strength of the material. Materials with high-strength properties are more resistant to deformation and damage during the layering and bonding process. Flexibility is another important property, as it impacts the ability of the material to conform to the desired shape and size.
Dimensional accuracy is also a critical factor in sheet lamination processes. Materials that do not maintain their dimensions throughout the process can result in poorly constructed final products. Additionally, the surface finish of the final product is influenced by the properties of the materials used. The smoother the surface finish, the more attractive and functional the final product.
In summary, the importance of material properties and performance in sheet lamination processes cannot be overstated. By understanding the role of properties like strength, flexibility, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish, manufacturers can optimize their processes to achieve high-quality final products.
Purpose of the post: to explore the properties and performance of sheet lamination materials in detail
This post explores sheet lamination material properties and performance in detail. Knowing these properties is crucial to successful lamination, affecting strength, flexibility, accuracy, and surface finish.
By exploring the properties of different materials used in sheet lamination, we can better understand their strengths and limitations. This knowledge can be used to optimize the process, improve the quality of the final product, and expand the range of materials that can be used in sheet lamination.
In addition, we will highlight the importance of material properties in sheet lamination and how they impact the process. For instance, materials with high-strength properties can withstand the layering and bonding process, while flexible materials can conform to the desired shape and size. Understanding these properties is essential for selecting the right materials and optimizing the sheet lamination process.
In summary, by exploring the properties and performance of sheet lamination materials, we can gain valuable insights into how to optimize the manufacturing process and achieve high-quality final products.
Types of Sheet Lamination Materials
A flexible additive manufacturing technique with several advantages is sheet lamination. The selection of materials is one of the most crucial aspects of this procedure’s success. The qualities of materials affect the final product’s strength, flexibility, dimensional correctness, and surface polish. This section will discuss materials used in sheet lamination, like ceramics, metals, composites, and plastics. Understanding these materials helps to select the best for the application, streamline production, and produce high-quality finished goods.
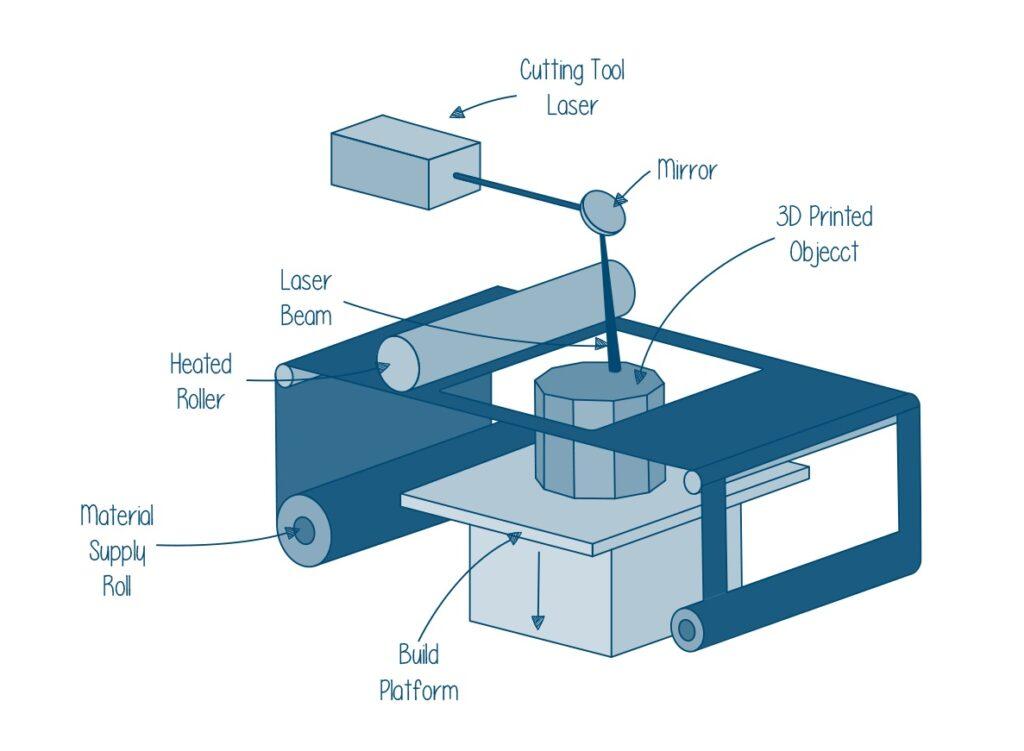
Overview of different types of materials used in sheet lamination, such as paper, metal foils, and plastics
In order to create high-quality finished goods, sheet lamination is a flexible manufacturing method that can use a range of materials. Some of the materials that are most frequently used in sheet lamination are paper, plastic, and metal foils.
Because it is inexpensive, lightweight, and flexible, paper is a great material for sheet lamination. It is frequently utilized by businesses in the packaging, printing, and bookbinding sectors.
Due to their strength, durability, and processing simplicity, plastics, especially thermoplastics, are also common materials for sheet lamination. They are perfect for creating intricate geometries since they can be shaped into a variety of sizes and forms.
Due to their excellent conductivity and robustness, metal foils like aluminum and copper are also employed in sheet lamination. To create conductive pieces, they are frequently employed in the electrical and electronic sectors.
The final product’s required qualities and the individual application determine the material to be used in sheet lamination. Manufacturers can select the ideal material for their unique demands and produce high-quality finished goods by studying the properties and features of various materials.
Properties of each type of material, including strength, flexibility, and thermal properties
In this section, we will examine the properties of different types of materials used in sheet lamination, including paper, plastic, and metal foils. Each material has its unique set of properties that affect the final product’s strength, flexibility, and thermal properties.
Paper is known for its low cost and easy availability, but it has lower strength and heat resistance compared to other materials. In contrast, plastic materials are lightweight and durable, with good flexibility and heat resistance. Metal foils have excellent strength and thermal properties, but they are less flexible than other materials.
Overall, the choice of material for sheet lamination depends on the specific application’s requirements and the desired properties of the final product. By understanding the unique properties of each material, we can make informed decisions about material selection in sheet lamination processes.
Performance characteristics of each material, including dimensional accuracy and surface finish
Different types of sheet lamination materials have unique performance characteristics. For example, paper-based materials offer good dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making them ideal for printing applications. Plastics are often chosen for their flexibility and durability and can be customized to achieve specific properties such as stiffness or heat resistance. Metal foils offer excellent strength and thermal properties, but may require additional processing steps for accurate dimensional control. It is important to consider the specific performance requirements of each application when selecting a sheet lamination material.
Material Selection for Sheet Lamination
The selection of materials is a crucial aspect of sheet lamination processes. When choosing a material, several factors must be considered, such as cost, availability, and required properties. In this section, we will explore the various materials used in sheet lamination and compare them based on their properties and performance characteristics. We will also examine case studies of successful applications of different materials in sheet lamination processes. By the end of this section, you will have a better understanding of how to choose the right material for your sheet lamination project.
Factors to consider when selecting a material for sheet lamination, including cost, availability, and required properties
When selecting a material for sheet lamination, it is important to consider various factors such as cost, availability, and required properties. Cost includes not only the material cost but also the cost of processing and finishing. Availability refers to the ease of acquiring the material in the required form and quantity. Required properties can vary depending on the specific application, and may include strength, flexibility, thermal stability, and dimensional accuracy. These factors should be balanced to select the optimal material for the intended use.
Comparison of different materials based on their properties and performance characteristics
Additionally, it is important to compare different materials based on their properties and performance characteristics. For example, paper is cost-effective and easy to print on, but may lack the strength and durability required for certain applications. Metal foils can provide high strength and thermal conductivity, but may be expensive and difficult to shape. Plastics offer a range of properties and can be cost-effective, but may require specialized processing and may have limited recyclability.
Case studies of successful applications of different materials in sheet lamination processes
Case studies of successful applications of different materials in sheet lamination processes can also provide valuable insights. By considering the factors involved in selecting materials and analyzing real-world examples, designers and manufacturers can make informed decisions to achieve the desired performance and cost outcomes.
Material selection is a critical factor in sheet lamination processes. To further illustrate the importance of selecting the right material, case studies can provide real-world examples of successful applications. A company can use recycled paper for laminating products, reducing waste and cost as a case study for paper materials. A manufacturer can pick a polymer for flexibility and durability. This results in high-quality plastic products. A company can use aluminum foil for thermal properties. It leads to improved performance in metal foil materials. Case studies help us understand material selection’s impact on sheet lamination success.
Material Properties and Performance in Sheet Lamination Processes
Sheet lamination is a popular manufacturing process that involves layering thin sheets of material to create a final product. The properties and performance of the materials used in this process play a crucial role in determining the quality and efficiency of the end product. In this section, we will explore the impact of material properties and performance on the sheet lamination process, from slicing to bonding to finishing. We will also provide tips for optimizing material properties for specific applications, and present a table of the key properties of paper, plastic, and metal foil materials commonly used in sheet lamination.
Overview of the sheet lamination process and its key steps
Sheet lamination is a process that involves stacking layers of material and then bonding them together. This process consists of several key steps, including slicing, bonding, and finishing. The properties of the materials used in the process can impact each of these steps, ultimately affecting the quality of the final product.
Discussion of how material properties and performance impact each step of the process, from slicing to bonding to finishing
Paper materials have various properties like thickness, strength, and porosity that affect the ease of slicing and bonding. Flexibility, durability, and thermal properties are important factors to consider for plastic materials during the bonding and finishing processes. The properties of metal foil materials like thickness, thermal conductivity, and surface finish have an impact on the final product’s quality.
Tips for optimizing material properties and performance for specific applications
To optimize material properties and performance for specific applications, it is important to carefully consider the requirements of the process and the desired characteristics of the final product. For example, a thicker paper material may be more suitable for a product that requires greater strength, while a thinner material may be more appropriate for a product that requires greater flexibility.
The table below provides an overview of the specific material properties that are important for sheet lamination processes in the paper, plastic, and metal foil categories:
| Material | Key Properties |
|---|---|
| Paper | Thickness, strength, porosity |
| Plastic | Flexibility, durability, thermal properties |
| Metal foil | Thickness, thermal conductivity, surface finish |
By carefully selecting and optimizing material properties and performance, sheet lamination processes can produce high-quality products that meet the specific needs of various industries and applications.
Future Directions in Sheet Lamination Materials
In this section, we’ll talk about new developments in sheet lamination, such as nanocomposites and bio-based materials. Due to their sustainability and capacity for recycling, bio-based materials are gaining popularity as a viable option for sheet lamination. On the other hand, nanocomposites offer distinctive qualities including greater strength and higher heat conductivity. Additionally, we will look at how improvements in sheet lamination materials may affect additive manufacturing as a whole, including the possibility of accelerated production and enhanced product quality.
Discussion of emerging trends and new materials in sheet lamination, such as bio-based materials and nanocomposites
The use of sophisticated polymers and composites in sheet lamination materials is one future approach. These materials are perfect for usage in a range of applications since they have better performance qualities like increased flexibility and durability. Self-healing materials that can mend damage on their own are also gaining popularity since they can lengthen the lifespan of the finished product.
Consideration of how advancements in sheet lamination materials will impact additive manufacturing as a whole
The adoption of 3D printing technologies is another development in sheet lamination materials. In comparison to conventional sheet lamination techniques, 3D printing has a number of advantages due to its capacity to produce intricate geometries and unique designs. Additionally, the sheet lamination sector is anticipated to undergo a revolution because of the usage of intelligent materials, such as those that can alter the shape or react to stimuli.
It is possible that we will observe a shift toward more sustainable and ecologically friendly solutions as sheet lamination materials continue to develop. This could involve the creation of closed-loop recycling systems or the usage of biodegradable materials. In the end, continual progress in material science and engineering, as well as a continued emphasis on innovation and sustainability, will determine the future of sheet lamination materials.
Conclusion
This post’s conclusion emphasized the significance of material performance and properties in sheet lamination and additive manufacturing. The effect of material qualities on the various steps of the sheet lamination process, such as slicing, bonding, and finishing, is one of the key points. In addition, new developments and materials were discussed, including nanocomposites and bio-based materials.
Recap of key points covered in the post
- Sheet lamination is an important process in additive manufacturing that involves bonding layers of material together to create a final product.
- Material properties such as thickness, strength, flexibility, and thermal conductivity play a crucial role in the sheet lamination process.
- Different materials, including paper, plastic, and metal foil, have unique properties and performance characteristics that impact their suitability for sheet lamination applications.
- Advancements in sheet lamination materials, including bio-based materials and nanocomposites, are driving new trends in additive manufacturing.
- Optimizing material properties and performance for specific applications is essential for achieving high-quality sheet lamination products.
- It is important for readers to continue learning about sheet lamination materials and their applications to stay up to date with emerging trends and advancements in the field.
Importance of material properties and performance in sheet lamination and additive manufacturing more broadly
Material properties and performance are critical factors in sheet lamination and additive manufacturing. The properties of the material used can significantly impact the final product’s quality and durability. For instance, in sheet lamination, the material’s thickness, porosity, and strength can affect the slicing and bonding processes, while in additive manufacturing, material properties like mechanical strength and thermal conductivity can impact the object’s performance. Therefore, understanding and optimizing the material properties and performance is crucial for achieving desired results in these manufacturing processes. In conclusion, the importance of material properties and performance cannot be overstated in sheet lamination and additive manufacturing more broadly.
Call to action for readers to continue learning about sheet lamination materials and their applications
Readers are urged to stay current on developments in the field and to experiment with various materials for their own projects in order to continue learning about sheet lamination materials and their applications. Manufacturers can boost the performance and quality of materials to produce products more effectively and with higher-quality additive manufacturing.
How to choose between different types of sheet lamination materials such as paper, plastic, and metal foil?
- Determine the specific requirements for the application
Identify the specific needs for the product, such as desired finish, strength, flexibility, and thermal properties.
- Evaluate the material properties of each option
Research and compare the properties of paper, plastic, and metal foil materials, such as thickness, strength, porosity, flexibility, thermal conductivity, and surface finish.
- Consider the cost and availability of each material
Evaluate the cost and availability of each material option, considering factors such as raw material cost, production costs, and supply chain logistics.
- Assess the environmental impact of each material
Consider the environmental impact of each material option, such as the use of recycled or bio-based materials.
- Determine the feasibility of processing each material
Evaluate the processing requirements and limitations of each material option, including slicing, bonding, and finishing processes.
- Make an informed decision based on the evaluation
Weigh the pros and cons of each material option and make an informed decision based on the specific needs of the application, material properties, cost, availability, environmental impact, and processing feasibility.
FAQs
Sheet lamination is a type of additive manufacturing process that involves layering thin sheets of material, such as paper, plastic, or metal foil, on top of each other and bonding them together to create a 3D object.
The most important material properties to consider in sheet lamination are thickness, strength, porosity, flexibility, durability, thermal properties, and surface finish.
Yes, it is possible to use different types of sheet lamination materials together in the same project, as long as they can be bonded together successfully and the combination of properties meets the required specifications.
To optimize material properties and performance for a specific sheet lamination application, you should first consider the requirements and specifications of the project. Then, choose materials that meet those specifications and make adjustments to the lamination process, such as adjusting the temperature or pressure, to achieve the desired result.
Some emerging trends in sheet lamination materials include the use of bio-based materials and nanocomposites, as well as advancements in the development of new polymers and metals for lamination.