Exploring the World of 3D Print Rubber: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
A cutting-edge substance utilized in the 3D printing process is 3D printing rubber. It has distinctive qualities that distinguish it from other materials. This article will provide an in-depth overview of the 3D print rubber industry. This tutorial will explain what 3DP rubber is, how it functions, its benefits and drawbacks, applications, procedures, and future potential, whether you’re a novice or an expert 3D printing fan. So let’s go in and discover the fascinating world of 3DP rubber together!
Brief overview of the topic
The world of 3D printing has undergone a transformation thanks to a material called 3D print rubber. It is a distinctive material with adaptable qualities that may be utilized to produce a range of patterns. The technology has been around for a while, but it has only recently acquired prominence. Designers may now make complex, supple, and flexible designs that were before impossible with 3DP rubber. This tutorial will examine the numerous facets of 3DP rubber, including its definition, operation, benefits, drawbacks, uses, procedures, and prospects in the future.
What is 3D print rubber and its use?
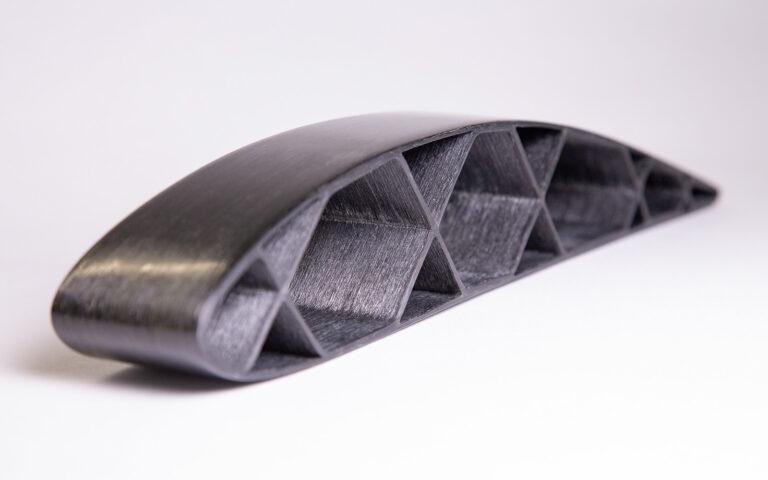
3D print Rubber is a material used in 3D printing consisting of rubber polymers. Its distinctive qualities make it a preferred option across a wide range of industries. It is adaptable, strong, and resistant to tearing. Also, the substance is simple to work with and is compatible with the majority of 3D printers.The fashion sector, the medical industry, and the automotive industry use it to make soft, flexible accessories, braces and prostheses, and flexible parts, respectively. The material has expanded 3D printing’s potential, making it a flexible and creative technology.

What is 3D print rubber?
Many people associate 3D printing with solid, hard materials like metal or plastic. But, since its inception, 3D printing has advanced significantly, and it is now possible to print materials like rubber. Rubber is a thermoplastic elastomer, a substance containing both rubber-like and plastic-like qualities. It is ideal for making soft, flexible items that must be able to bend and stretch because of its high flexibility and durability. We’ll look into what 3D print rubber is, how it’s created, and how it differs from other 3D printing materials in this section.
Definition of 3D print rubber
In 3D printing, people use a form of thermoplastic elastomer called 3D print rubber. Manufacturers create this flexible material using rubber polymers, which give it qualities similar to both rubber and plastic. Most 3D printers are highly compatible with this material, and it can be produced in several ways. The material melts into a liquid state during the printing process, and the printer extrudes it layer by layer to create the desired shape. The substance solidifies and keeps its shape after cooling. The end result is a strong, long-lasting, and wear-resistant object.
Types of 3D print rubber materials
Several types of rubber materials exist for 3D printing, and one of the most commonly used is thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). They are a blend of rubber and plastic materials and are highly flexible and durable. Another type of rubber material used in 3D printing is thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). TPU maintains its shape even when stretched or bent, making it a highly elastic material. Another rubber material used in 3D printing is flexible resin, which is a liquid resin that cures through light exposure, resulting in a flexible and durable object.
Properties and characteristics of 3D print rubber
A common material for 3D printing, 3D print rubber features a number of distinctive qualities and traits. One of its primary characteristics is flexibility, which enables the production of soft, flexible forms that can bend and stretch without breaking. It is also excellent for constructing products that must withstand repeated usage because it is extremely strong and resistant to wear and strain. Extrusion and light-curing are two methods for printing 3D print rubber, which is also simple to deal with. The capacity to hold its shape, compatibility with the majority of 3D printers, and excellent adherence to other materials are further qualities of 3D print rubber.
| Property/Characteristic | TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Very High | High |
| Durability | High | High |
| Resistance to wear and tear | High | High |
| Shore hardness (Durometer) | 60-80A | 60-80A |
| Printing temperature range (°C) | 200-230 | 200-240 |
| Printing speed | Moderate | Moderate |
| Compatibility with 3D printers | High | High |
| Chemical resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Transparency | Transparent | Opaque |
How does 3D print rubber work?
After discussing what 3D print rubber is and how it functions, let’s move on to its characteristics. Rubber 3D printing uses a procedure that is similar to that of other materials, but there are some significant distinctions. To construct the required shape, you heat the material until it becomes liquid and then extrude it one layer at a time. However, because the material is flexible, you need precise printing settings and methods to ensure good adherence and avoid warping. In this section, we’ll examine the distinctions between 3D printing with rubber and other materials, the important aspects to take into account when 3D printing with rubber, and an overview of the rubber 3D printing procedure.
Overview of the 3D printing process with rubber
The 3D printing process with rubber typically involves using a Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printer. The printer heats the rubber filament to a specific temperature, melting it into a liquid form. The 3D printer extrudes the melted rubber through a nozzle and deposits it onto a build platform, layer by layer. To guarantee the structural integrity of the printed object, the printer may use support structures, which the operator can remove after the printing is complete. After the printing process, the object is cooled and the operator removes it from the build platform. Compared to 3D printing with other materials, printing with rubber requires careful calibration and adjustments to ensure the correct printing temperature and speed.
Differences between 3D printing with rubber and other materials
Each material has specific properties and printing needs when it comes to 3D printing. Rubber 3D printing differs significantly from other materials, mostly because of its flexibility and softness. Rubber needs a different strategy than rigid materials in order to ensure appropriate adhesion, prevent warping, and obtain the desired level of flexibility. The distinctions between 3D printing with rubber and other materials will be discussed in this section. We’ll also examine the particular difficulties and limitations associated with 3D printing with rubber and how they affect the printing procedure.
Key factors to consider when 3D printing with rubber
When 3D printing with rubber, it’s crucial to take a few important aspects into account in order to get the finest results. Rubber, unlike other materials, necessitates certain printing settings and methods to provide adequate adhesion, avoid warping, and obtain the desired level of flexibility. The important things to take into account when 3D printing with rubber will be discussed in this section. We’ll go over the most important factors to help you get the greatest outcomes from your 3D printing projects, from printing temperature and speed to post-processing and filament storage. These criteria will assist you in getting the greatest results while working with rubber, regardless of whether you are a novice or an expert 3D printer.
The printing temperature and speed
When 3D printing with rubber, temperature, and speed are critical factors to consider. Rubber requires a lower printing temperature than other materials, usually between 190-220°C. Printing speed should also be slower to allow the material to cool before the next layer is added. This helps prevent warping and ensures that the layers adhere correctly.
Bed adhesion
Bed adhesion is an important factor to consider when 3D printing with rubber. Due to its flexibility, rubber has a tendency to warp or move during the printing process. Using a heated bed and a specialized adhesive surface like a BuildTak or a Kapton tape can help ensure proper bed adhesion and prevent warping.
Design considerations
Design considerations are also important when 3D printing with rubber. Designers should optimize designs for flexibility and consider any necessary support structures due to the material’s flexibility. The design should also consider the strength of the material and the purpose of the final product.
Material properties
The properties of the rubber material being used should also be considered when 3D printing. Different types of rubber have different durometers or levels of hardness, and this can affect the flexibility of the final product. Additionally, the chemical and heat resistance of the material should also be taken into account, depending on the intended application of the final product.
Printing techniques
Finally, printing techniques can also impact the quality of the final product. Techniques such as reducing the printing speed for the first few layers, increasing the number of perimeters, and using a higher infill percentage can help improve the adhesion and strength of the final product.
Support structures
Support structures are essential when 3D printing with rubber. Since rubber is a flexible material, it may require additional support structures to prevent it from warping or moving during the printing process. These support structures should be designed to be easily removable after printing.
Post-processing
Post-processing is also an important factor to consider when 3D printing with rubber. Since rubber is a flexible material, it may require additional post-processing steps, such as annealing or polishing, to achieve the desired level of flexibility and surface finish.
Quality of the printer
The quality of the printer used for 3D printing with rubber is also important. High-quality printers with advanced features like a direct drive extruder or a heated chamber can improve the printing quality and reduce the likelihood of warping or adhesion issues.
Filament storage
The storage of rubber filament is another important factor to consider. Rubber filament can absorb moisture from the air, which can affect the printing quality and cause issues like bubbling or warping. To prevent this, the filament should be stored in a dry and cool place, away from moisture and direct sunlight.
Testing and iteration
Finally, testing and iteration are important when 3D printing with rubber. Due to the material’s unique properties, it may require several iterations to achieve the desired level of flexibility, strength, and surface finish. It’s important to test and iterate the design, printing settings, and post-processing steps to achieve the best possible results.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D print rubber
Rubber offers a number of distinct advantages and disadvantages when it comes to 3D printing when compared to other materials. The advantages of employing 3D print rubber, such as its adaptability, toughness, and simplicity of usage, will be discussed in this part. We’ll also discuss some disadvantages of using 3D print rubber, such as the possibility of warping and the requirement for specific printing parameters. Finally, in order to help you comprehend the special advantages and disadvantages of working with rubber, we’ll compare 3D print rubber to other 3D printing materials. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of 3D print rubber will help you make better decisions regarding your printing projects, whether you’re a novice or a seasoned 3D printer.
Benefits of using 3D print rubber
Flexibility
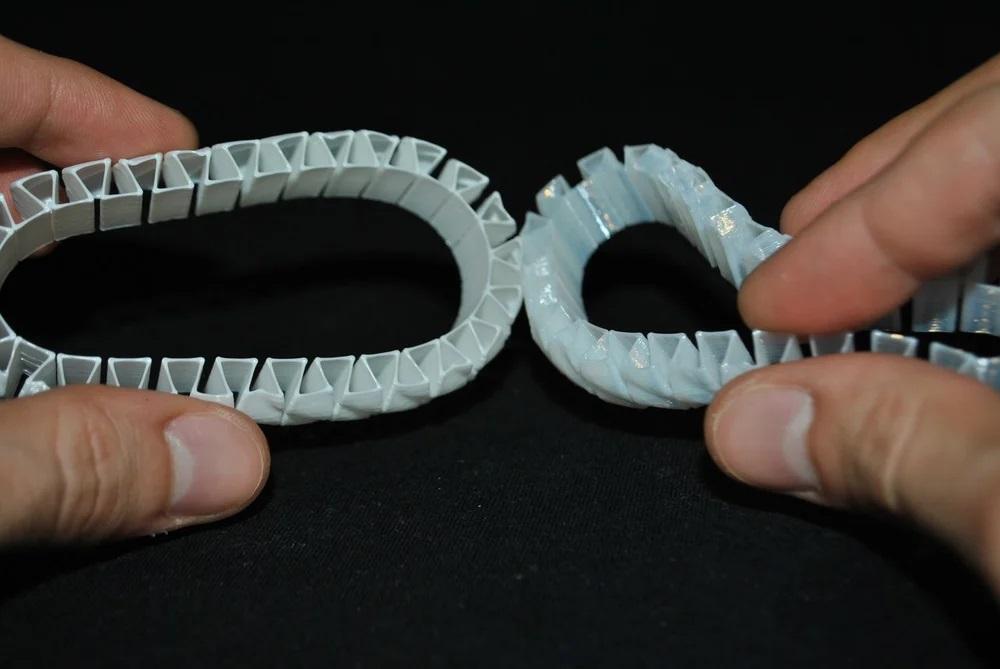
One of the most significant benefits of using 3D print rubber is its flexibility. Rubber is a soft and pliable material that can bend and stretch without breaking, making it ideal for applications that require flexibility or shock absorption. 3D printing with rubber allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other materials.
Durability
Rubber is also a durable material that can withstand wear and tear over time. It’s resistant to abrasion, impact, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for applications that require strength and durability. 3D printing with rubber allows for the creation of durable and long-lasting parts that can withstand a wide range of conditions.
Ease of use
3D print rubber is also relatively easy to use compared to other materials. It requires minimal post-processing and can be printed with a standard 3D printer, making it accessible to a wider range of users. It also has a low melting point, which means it can be printed at lower temperatures than other materials, reducing the likelihood of warping or adhesion issues.
Wide range of applications
3D print rubber has a wide range of applications, from creating flexible phone cases and shoe soles to manufacturing industrial parts and medical devices. Its flexibility and durability make it ideal for applications that require shock absorption, sealing, or cushioning. It’s also used in prototyping and product development, allowing for the creation of functional prototypes and mockups.
Cost-effective
Finally, 3D print rubber can be a cost-effective alternative to other materials, especially in low-volume production runs or prototyping. Since it requires minimal post-processing and can be printed with standard 3D printers, it can be a more cost-effective option than traditional manufacturing methods.
Drawbacks of using 3D print rubber
Warping
One of the drawbacks of using 3D print rubber is the potential for warping during the printing process. Rubber has a tendency to warp or move during printing, especially if the printing temperature is too high or if there’s not enough bed adhesion. This can result in a finished product that doesn’t adhere correctly or has an uneven surface.
Difficulty in printing
Another challenge of using 3D print rubber is the difficulty in printing. Rubber is a flexible material that can be challenging to work with, especially for beginners. It requires specialized printing settings and techniques to ensure proper adhesion and prevent warping. Printing with rubber may also require additional support structures to prevent the material from moving during printing.
Limited color options
3D print rubber is also limited in terms of color options. While some manufacturers offer a variety of colors, most rubber filaments are only available in black or white. This can be a drawback for users who want to create colorful or custom-designed products.
Less precision
Another drawback of using 3D print rubber is that it may offer less precision than other materials. Due to its flexibility and softness, rubber may not be suitable for creating parts with high levels of detail or accuracy. This can be a limitation for users who require high precision in their products.
Limited chemical resistance
Finally, 3D print rubber may have limited chemical resistance compared to other materials. Rubber may not be suitable for applications that require resistance to harsh chemicals or solvents. Users should carefully consider the intended application of their final product before choosing to print with rubber.
Comparison of 3D print rubber with other 3D printing materials
Comparison with PLA
Compared to PLA, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and durability. While PLA is a rigid material that can be brittle and prone to breaking, rubber can bend and stretch without breaking. However, PLA may offer better printing precision and is easier to work with, especially for beginners. PLA also has a wider range of color options and is more environmentally friendly than rubber.
Comparison with ABS
Compared to ABS, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and impact resistance. ABS is a rigid material that can be brittle and prone to breaking under stress, while rubber can bend and absorb impact. However, ABS offers better heat resistance and is more suitable for applications that require high temperatures. ABS may also offer better printing precision and is easier to work with than rubber.
Comparison with PETG
Compared to PETG, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and durability. PETG is a rigid material that can be brittle and prone to breaking, while rubber can bend and stretch without breaking. However, PETG offers better chemical resistance and is more suitable for applications that require resistance to solvents and chemicals. PETG may also offer better printing precision and is easier to work with than rubber.
Comparison with Nylon
Compared to Nylon, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and durability. Nylon is a rigid material that can be brittle and prone to breaking under stress, while rubber can bend and absorb impact. However, Nylon offers better printing precision and is easier to work with, especially for beginners. Nylon is also more suitable for applications that require high strength and durability.
Comparison with Polypropylene (PP)
Compared to Polypropylene, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and impact resistance. Polypropylene is a rigid material that can be brittle and prone to breaking under stress, while rubber can bend and absorb impact. However, Polypropylene offers better chemical resistance and is more suitable for applications that require resistance to solvents and chemicals. Polypropylene may also offer better printing precision and is easier to work with than rubber.
Comparison with Polycarbonate
Compared to Polycarbonate, 3D print rubber offers superior flexibility and ease of printing. Polycarbonate is a rigid material that can be difficult to print due to its high melting point and tendency to warp. Rubber, on the other hand, has a low melting point and requires minimal post-processing. However, Polycarbonate offers better strength and heat resistance, making it more suitable for applications that require high temperature and impact resistance. Polycarbonate may also offer better printing precision and is more suitable for creating parts with high levels of detail.
Applications of 3D print rubber
3D print rubber has a wide range of applications in various industries. Its flexibility and durability make it suitable for applications that require shock absorption, cushioning, and sealing. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical use 3D print rubber to create functional prototypes, custom parts, and low-volume production runs. Examples of 3D print rubber applications include phone cases, shoe soles, and industrial parts. Creative users have also found unique applications for 3D printing rubber, such as creating custom stamps or artistic sculptures. The versatility and range of applications make 3D print rubber a valuable tool for many industries and users.
Industries that use 3D print rubber
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a major user of 3D print rubber. Rubber parts such as gaskets, seals, and hoses can be 3D printed, reducing the need for expensive tooling and molds. Automakers can also use 3D print rubber to create custom parts for prototype vehicles. For example, Ford used 3D print rubber to create a custom sealing gasket for a transmission oil pan. The gasket was designed to reduce oil leaks and improve fuel efficiency.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry is another major user of 3D print rubber. Rubber parts such as seals and gaskets can be 3D printed for use in aircraft engines and other critical components. For example, NASA used 3D print rubber to create a seal for a valve on the International Space Station. The seal was designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures of space.
Medical Industry
The medical industry is a growing user of 3D print rubber. Medical devices such as prosthetics, orthotics, and hearing aids can be 3D printed using rubber materials. 3D print rubber is also used to create anatomical models for surgical planning and training. For example, a company called TriFusion Devices used 3D print rubber to create a custom prosthetic leg for a dog. The leg was designed to be lightweight and flexible, allowing the dog to move more comfortably.
Sporting Goods Industry
The sporting goods industry is another user of 3D print rubber. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create custom shoe soles, grips, and other components. For example, Adidas used 3D print rubber to create a custom midsole for their Futurecraft 4D running shoe. The midsole was designed to provide a comfortable and supportive fit for runners.
Consumer Goods Industry
Finally, the consumer goods industry is a major user of 3D print rubber. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create phone cases, watch bands, and other accessories. For example, a company called Loctite used 3D print rubber to create a custom phone case that was shock-resistant and offered superior grip.
Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturing is a growing user of 3D print rubber. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create custom parts, prototypes, and molds. For example, a company called Ohio Rubber used 3D print rubber to create a custom mold for a rubber gasket. The mold was designed to reduce production time and costs.
Architecture and Design
The architecture and design industry is also using 3D print rubber for creating unique and functional designs. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create decorative features, furniture, and other design elements. For example, designer Oluwaseyi Sosanya used 3D print rubber to create a custom light fixture for a hotel in London. The fixture was designed to mimic the texture of coral, creating a visually stunning and functional piece.
Education and Research
3D print rubber is also being used in education and research. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create anatomical models for teaching and research purposes. For example, researchers at the University of Michigan used 3D print rubber to create a model of a heart valve. The model was designed to help surgeons practice minimally invasive valve replacement procedures.
Art and Fashion
Finally, 3D print rubber is being used in the art and fashion industries for creating unique and expressive designs. Rubber materials can be 3D printed to create sculptures, jewelry, and other artistic pieces. For example, artist Neri Oxman used 3D print rubber to create a series of sculptures inspired by natural forms. The sculptures were designed to showcase the potential of 3D print rubber in creating intricate and organic designs.
Creative uses of 3D print rubber
Custom Stamps
3D print rubber can be used to create custom stamps for a variety of applications. The rubber material allows for intricate designs to be easily printed and transferred onto various surfaces. These stamps can be used for arts and crafts, as well as for industrial applications.
Jewelry and Accessories
3D print rubber can be used to create unique jewelry and accessories that are flexible and comfortable to wear. Rubber materials can be printed in various colors and textures, allowing for a wide range of designs to be created. These accessories can be functional, such as phone cases, or purely decorative, such as earrings and bracelets.
Artistic Sculptures
3D print rubber can be used to create intricate and expressive sculptures. The flexibility and durability of the rubber material allow for complex shapes and forms to be printed. Artists can use 3D print rubber to create sculptures that are inspired by natural forms, such as plants and animals, or to explore abstract concepts and forms.
Architectural Models
3D print rubber can be used to create architectural models that are detailed and functional. Rubber materials can be printed to mimic the texture and appearance of building materials, such as concrete or stone. These models can be used for design and planning purposes, as well as for presentation and display.
Toys and Games
3D print rubber can be used to create custom toys and games that are safe and durable. Rubber materials can be printed to create soft and flexible toys that are safe for children to play with. These toys and games can be designed to be educational, such as puzzles and building blocks, or purely for entertainment, such as action figures and dolls.
Techniques for 3D printing with rubber
There are particular methods and factors that must be taken into account when 3D printing with rubber. These methods include setting up your 3D printer for rubber filament, learning how to print with rubber, and diagnosing typical problems that can occur during printing. This section will give an overview of the methods used in 3D printing with rubber, along with advice on how to get the best results. Understanding these methods will help you produce high-quality prints with rubber filament, regardless of whether you are new to 3D printing or an experienced user.
Preparing your 3D printer for rubber filament
Check your printer’s specifications
Before printing with rubber filament, it is essential to ensure that your 3D printer is compatible with the material. Check your printer’s specifications to ensure that it can handle rubber filament, including the recommended temperature range and nozzle size.
Clean your printer
Before printing with rubber filament, it is essential to clean your printer thoroughly. Any debris or residue in the printer’s nozzle or extruder can cause issues during the printing process. Use a cleaning filament or disassemble the extruder and nozzle to clean them thoroughly.
Adjust your printer settings
Printing with rubber filament requires different settings than printing with other materials. Adjust your printer’s settings to ensure that the temperature and speed are appropriate for the rubber material. You may also need to adjust your printer’s retraction settings to prevent the material from oozing.
Use a build plate adhesive
Rubber filament can be challenging to adhere to the build plate, so it is recommended to use a build plate adhesive. This adhesive can help keep the material in place during printing and prevent warping or shifting. Use a glue stick or a specialized adhesive, such as a rubber adhesive sheet, to ensure that the material sticks to the build plate.
Consider using a direct drive extruder
Direct drive extruders can be beneficial when printing with rubber filament. These extruders are positioned directly above the hot end, which can help to prevent issues such as clogging or the material oozing. Direct drive extruders also allow for more precise control over the material flow rate.
Use high-quality rubber filament
The quality of the rubber filament can have a significant impact on the final print’s quality. Choose a high-quality rubber filament that is specifically designed for 3D printing. These filaments are often more consistent in terms of thickness and elasticity, which can result in better print quality and fewer issues during the printing process.
Test your printer settings
Before starting a large print with rubber filament, it is recommended to perform a test print to ensure that your printer settings are appropriate. Use a small model or a calibration cube to test the settings and adjust as necessary before moving on to larger prints.
Store your filament properly
Rubber filament can be sensitive to moisture, so it is crucial to store it properly. Keep the filament in a dry, airtight container or bag to prevent exposure to humidity or moisture. Store the container or bag in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Tips for 3D printing with rubber
Slow down your print speed
Printing with rubber filament requires a slower print speed than other materials. Slower print speeds help to ensure that the material flows smoothly and reduces the risk of clogging or other issues. Experiment with different print speeds to find the optimal setting for your printer and the specific rubber filament you are using.
Use support structures
Printing with rubber filament can be challenging because it can be prone to warping or shifting during printing. Using support structures can help to keep the material in place and improve the overall print quality. Use support structures where necessary, such as for overhangs or complex shapes.
Adjust your cooling settings
Cooling can be an essential factor when printing with rubber filament. Too much cooling can cause the material to become brittle, while too little cooling can result in poor print quality. Experiment with different cooling settings to find the optimal temperature and airflow for your printer and the specific rubber filament you are using.
Keep an eye on the first layer
The first layer is critical when printing with rubber filament. It sets the foundation for the rest of the print and can significantly impact the final result. Keep an eye on the first layer to ensure that it adheres properly to the build plate and that the extrusion is consistent.
Use a heated build plate
Using a heated build plate can be beneficial when printing with rubber filament. The heat can help to improve the material’s adhesion to the build plate and reduce the risk of warping or shifting during printing. Experiment with different build plate temperatures to find the optimal setting for your printer and the specific rubber filament you are using.
Consider using a larger nozzle
Printing with rubber filament can be challenging due to the material’s flexibility and flow characteristics. Using a larger nozzle can help to improve the material flow and reduce the risk of clogging or other issues. Experiment with different nozzle sizes to find the optimal size for your printer and the specific rubber filament you are using.
Check your extruder tension
Extruder tension can play a crucial role in printing with rubber filaments. Too much tension can cause the material to stretch, while too little tension can result in under-extrusion or clogging. Check your extruder tension regularly to ensure that it is set correctly for the specific rubber filament you are using.
Clean your printer regularly
Regular cleaning of your printer can help to ensure that it is working optimally when printing with rubber filament. Clean the build plate, nozzle, and extruder regularly to prevent any buildup or blockages that can impact print quality.
Use high-quality rubber filament
Using high-quality rubber filament is critical when printing with this material. Inferior-quality filament can result in poor print quality, clogging, or other issues. Invest in high-quality rubber filament from reputable manufacturers to ensure that you get the best results.
Be patient and experiment
Printing with rubber filament can be challenging, and it may take some time to get the hang of it. Be patient, and don’t be afraid to experiment with different settings and techniques to find what works best for you and your printer. With some practice, you can achieve excellent results when printing with rubber filament.
Common issues and how to troubleshoot them
Clogging
Clogging is a common issue when printing with rubber filament, particularly if the material is low-quality or the printer is not set up correctly. To troubleshoot this issue, try increasing the extruder temperature, reducing the print speed, or using a larger nozzle size.
Under-extrusion
Under-extrusion can occur if the extruder tension is too low or if the filament is not feeding into the printer correctly. To troubleshoot this issue, check the extruder tension, clean the nozzle, and ensure that the filament is feeding smoothly into the printer.
Warping
Warping can occur when the print bed temperature is too low or when the printer is not calibrated correctly. To troubleshoot this issue, increase the print bed temperature, use a brim or raft for the print, or recalibrate the printer.
Layer separation
Layer separation can occur if the print bed temperature is too high or if the printer is not calibrated correctly. To troubleshoot this issue, reduce the print bed temperature, adjust the printer calibration, or use a different adhesive for the build plate.
Poor surface finish
Poor surface finish can occur if the printer settings are not optimized for rubber filament or if the printer is not set up correctly. To troubleshoot this issue, adjust the print speed, nozzle temperature, and extruder tension, or use a different rubber filament that is more compatible with your printer.
Stringing
Stringing can occur when the printer is retracting the filament too slowly or not retracting it at all. To troubleshoot this issue, try increasing the retraction distance and speed, adjusting the nozzle temperature, or using a different rubber filament.
Bulging
Bulging can occur when the printer is over-extruding the filament, causing it to expand beyond the intended size. To troubleshoot this issue, reduce the extruder temperature, increase the print speed, or adjust the printer settings to better accommodate the rubber filament.
Adhesion problems
Adhesion problems can occur when the rubber filament is not sticking to the build plate, causing the print to lift or detach. To troubleshoot this issue, clean the build plate thoroughly, use a different adhesive such as a glue stick or hairspray, or adjust the print bed temperature.
Inconsistent extrusion
Inconsistent extrusion can occur when the printer is not calibrated correctly or when the filament is not being fed evenly into the printer. To troubleshoot this issue, recalibrate the printer, check the extruder tension, and ensure that the filament is feeding smoothly into the printer.
Material compatibility issues
Material compatibility issues can occur when the rubber filament is not compatible with the printer or with other materials being used in the same print. To troubleshoot this issue, use a rubber filament that is specifically designed for your printer, and ensure that all materials used in the print are compatible with each other.
Future of 3D print rubber
Many possibilities abound for 3D printing rubber in the future. We may anticipate new and creative applications for rubber filament in many industries as technology develops. The flexibility, durability, and precision of 3D-printed rubber items may improve with the introduction of new materials and printing methods. The need for more environmentally friendly and sustainable materials, as well as the price and accessibility of 3D printing technology, are some of the difficulties that may need to be addressed. Despite these difficulties, the future of 3D print rubber appears promising, offering limitless potential for development and invention.
Predicted advancements in 3D print rubber technology
The technology behind rubber printing is continually changing, just like the rest of the 3D printing industry. In the upcoming years, the field of 3D print rubber technology is likely to experience considerable breakthroughs as scientists and engineers continue to experiment with novel materials and procedures. Improved rubber filaments that are stronger, more flexible, and simpler to print with, as well as new printing procedures that enable more intricate designs and higher levels of accuracy, may be among these developments. We can also anticipate a larger emphasis on creating specialized rubber printing applications for particular use cases as 3D printing is increasingly broadly used across industries.
New applications and industries that may emerge
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, we can expect to see new applications and industries emerge that utilize the benefits of rubber printing. From custom footwear to automotive parts and medical implants, the potential uses for 3D print rubber are nearly limitless. In particular, we may see an increased focus on creating rubber products that are not only durable and functional but also environmentally sustainable. As companies continue to invest in 3D printing technology, we can anticipate exciting new developments in the field of rubber printing that will benefit a wide range of industries and consumers alike.
Challenges that may need to be addressed
Although 3D print rubber technology has great potential, there are still issues that need to be solved before it can reach its full potential. Rubber can be a challenging material to work with, thus one of the main issues is assuring consistency in quality and accuracy in the printed products. However, there can be environmental issues with the usage of specific rubber compounds, as well as difficulties with scaling up manufacturing and making the technology more available and inexpensive to a larger range of sectors. In order to ensure the safe and sustainable growth of 3D print rubber technology, it will be crucial to properly address these issues, as with any newly emerging technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D print rubber has revolutionized the world of 3D printing, enabling the creation of complex designs with greater flexibility and durability. The benefits of using rubber filament are numerous, with applications across various industries and even in creative fields. While there are some challenges to overcome, such as the need for specialized equipment and the potential for printing issues, advancements in technology are likely to continue to address these challenges. As 3D print rubber becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see even more exciting applications emerge in the future.
Summary of key points
In summary, 3D printing with rubber materials presents unique opportunities and challenges. It offers benefits such as flexibility, durability, and customization for various industries and applications. However, there are also drawbacks and technical considerations that need to be addressed to achieve successful prints. By preparing the 3D printer properly, following tips and best practices, and troubleshooting common issues, high-quality rubber prints can be achieved. As technology advances, new applications and industries may emerge, and challenges may need to be addressed. Overall, 3D printing with rubber is a promising area of innovation with exciting potential for the future.
Final thoughts and recommendations for readers
In conclusion, 3D printing with rubber materials offers many benefits for various industries and applications. While there are some challenges to consider and techniques to master, the potential for creative and innovative uses is vast. As advancements in technology continue, we can expect to see even more exciting opportunities and applications emerge. For those interested in exploring 3D printing with rubber, it is important to carefully consider the key factors involved and seek out reliable resources for guidance. Overall, 3D printing with rubber holds significant promise and potential for those willing to invest the time and effort to explore its capabilities.
How to choose the right 3D printer for rubber printing?
- Determine your budget
Decide how much you’re willing to spend on a 3D printer for rubber printing.
- Research the market
Look at different models and brands of 3D printers that are capable of printing with rubber filaments.
- Check the printer specifications
Look for features such as a large build volume, heated bed, and compatibility with rubber filaments.
- Consider the print quality
Check out print samples and reviews to determine if the printer produces high-quality prints.
- Look for customer support
Ensure that the manufacturer provides good customer service and technical support.
- Consider the ease of use
Look for a 3D printer that is easy to set up and use, with a user-friendly interface.
- Evaluate the durability and maintenance
Check for reviews on the durability and reliability of the printer, as well as the ease of maintenance.
- Compare prices and choose the best option
Once you have considered all the factors, compare prices and choose the 3D printer that best fits your needs and budget.
FAQs
The main advantages of 3D printing with rubber are its flexibility, durability, and ability to create complex and intricate shapes.
Yes, there are some downsides to 3D printing with rubber, such as the difficulty in achieving fine details and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
No, not all 3D printers are capable of printing with rubber. You need to choose a 3D printer that is specifically designed for rubber printing or has the ability to print with flexible materials.
Common issues when 3D printing with rubber include under-extrusion, warping, and poor bed adhesion. You can troubleshoot these issues by adjusting the temperature, increasing the bed adhesion, and using support structures.