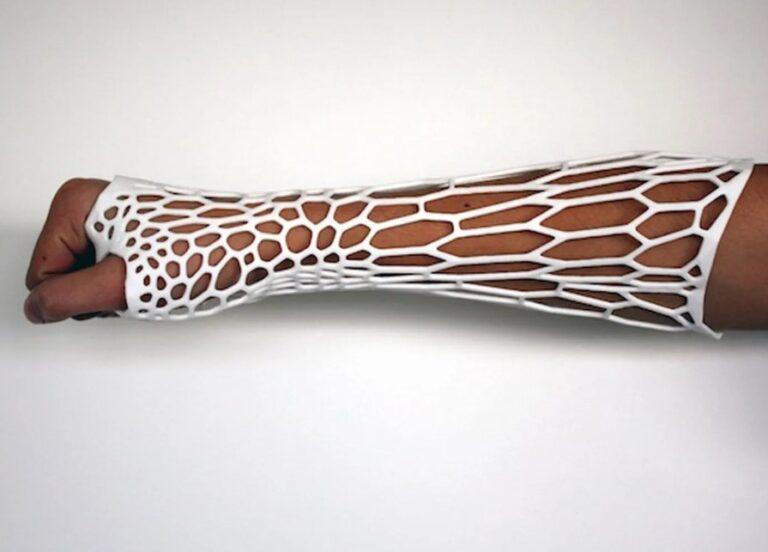
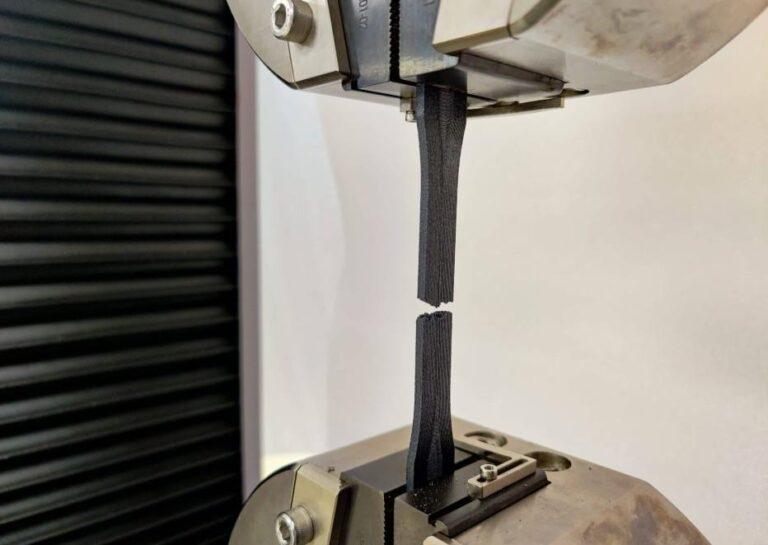
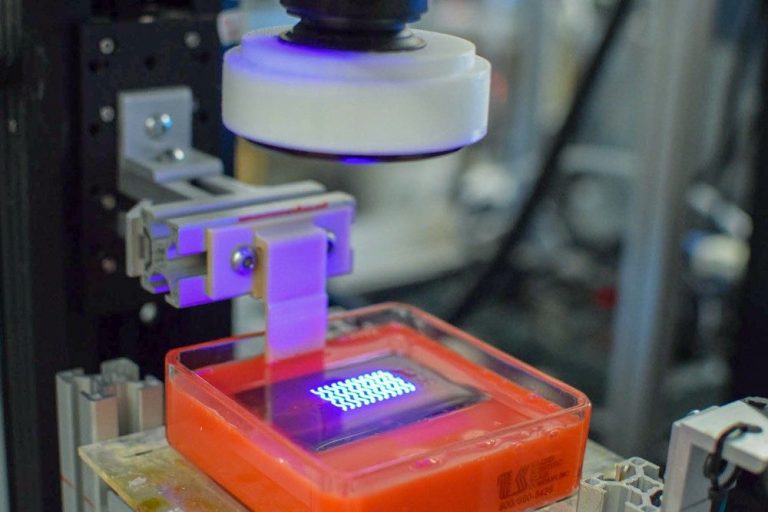
A resin 3D printer is a unique machine that has the ability to print highly detailed and functional plastic objects. This opens the doors for endless possibilities in manufacturing applications. Resin 3D printing is a great way to create prototypes, replacement parts, tools, and more for your home or office. Resin 3D printing has endless possibilities for applications in almost every industry. 3D printing with resin can make you imagine what was once not possible.
A popular choice for anyone interested in creating highly-detailed models that would be impossible to begin using a filament-fed, FDM 3D printer, resin 3D printers have become increasingly popular as 3D printing becomes more affordable and accessible. A Masked Stereolithography resin 3D printer, or MSLA printer, usually has a single axis of motion. A simple and inexpensive design allows these resin 3D printers to be less than $300.
The best resin 3D printers can make high-resolution models with a UV light source and resin. MSLA printers use a masking LCD to block the UV light pixel-by-pixel selectively. This resolution can be .035mm down the XY axes. 3D printers that use resin can produce high-definition designs at the cost of needing to be post-processed afterward. Never leave UV resin exposed to UV light for long periods. UV resin requires vigilance while handling.
What is SLA Resin 3D Printing?
Stereolithography was the world’s first 3D printing technology, invented in the 1980s, and is currently one of the most popular technologies for professionals. Resin SLA 3D printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into rigid plastic in a process called photopolymerization.
SLA resin 3D printers have grown hugely popular for their capacity to generate high-accuracy, isotropic, and waterproof prototypes and parts in a range of sophisticated materials with fine details and excellent surface finish. SLA’s resin formulas offer a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal qualities to match ordinary, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
Resin 3D printing is a fantastic alternative for highly detailed prototypes needing tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, such as molds, patterns, and functional parts. SLA 3D printers are a rapidly growing field with many uses. These uses include engineering and product design, manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model building, education, etc.
FDM vs. SLA resin 3D printer
When additive manufacturing technologies generate parts layer by layer, each layer also provides a chance for error. The technique used to build up the layers during printing affects each layer’s surface quality and precision, and thus the quality of the final print.
FDM 3D printers build layers by depositing lines of molten material. With this method, The model’s resolution depends upon the size of the extrusion nozzle, and there are gaps between the rounded lines laid down by the nozzle. As a result, the layers of the 3D model may not entirely adhere to one another, so the surface of the model is not as smooth as with other techniques.
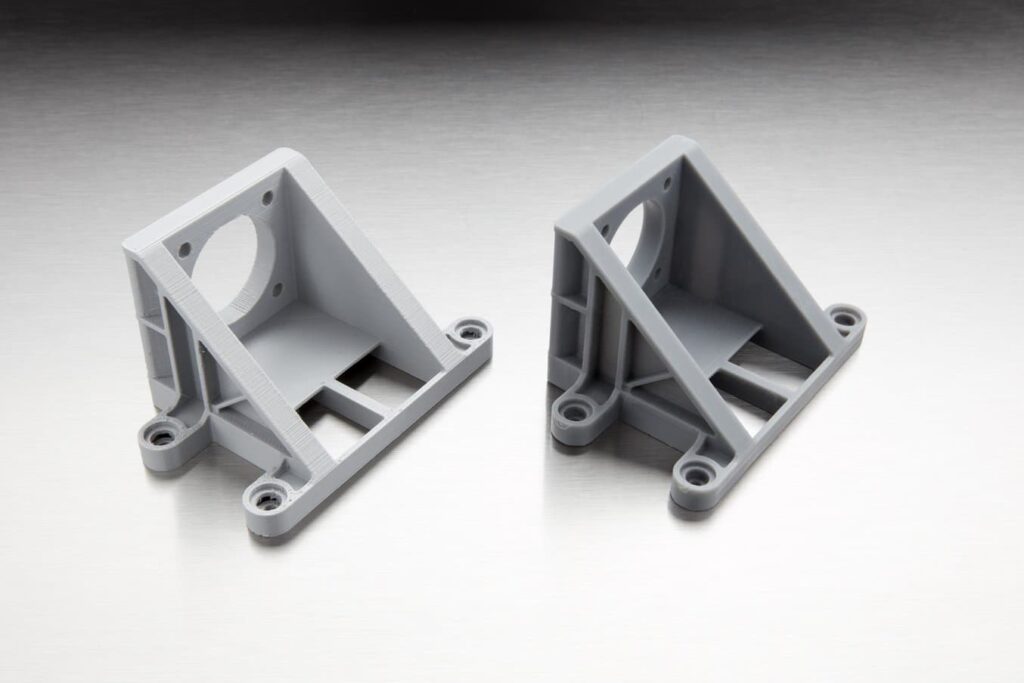

SLA 3D printing uses a high-precision laser that cures liquid resin to build each layer. This process can create intricate details and consistently produces high-quality models. SLA 3D printing results in tiny features, smooth surface finish, and extreme precision.
Another method SLA printers use is light and heat because the 3D print objects at room temperature don’t suffer from thermal expansion and contraction issues that happen when printing with FDM methods.
While FDM printers make a mechanical bond between layers, SLA 3D printers create chemical bonds by cross-linking photopolymers between layers, resulting in entirely dense components that are water and airtight. These connections give high degrees of lateral strength, resulting in isotropic components, meaning that the strength of the parts does not alter with orientation. These isotropic details make SLA 3D printing especially appropriate for engineering and industrial applications where material qualities matter.
Comparison of Filament and Resin Printers
There are numerous crucial things to consider when determining whether an FDM or SLA/DLP printer is the ideal solution for you.
Cost
When acquiring a 3D printer, it is not just the printer cost that you must consider; it is the filament or resin cost and additional accessories and time needs. FDM printers readily win over SLA/DLP printers at every level on printer cost. Especially for newbies, budget and entry-level SLA/DLP printers are few and far between. In addition, you must consider the care of the printer. A spool of filament will cost you $25 or less, with infrequent nozzle replacement provided proper cleaning and maintenance. You will need to refill both resin and resin tanks with resin printers periodically. A tank costs $40 or so, and a liter of resin is roughly $80. When comparing expenses, an FDM printer is significantly more economical.
Quality
A crucial factor in 3D printing is the quality of things you create. FDM printers rely on various elements, such as extruder accuracy, nozzle size, and adhesion between layers. Warping, shrinking, and shifting are not unusual as the layers are gently pressed together. But these flaws are often cleared in post-processing. On the other hand, SLA/DLP printers give exceptional quality since the laser decides minute details, resulting in incredibly accurate, high-quality print outputs. When comparing finished objects, resin 3D printing gives superior ultimate outcomes.
Ease of Use
There is a distinct learning curve no matter if you use a filament or resin 3D printer. For filament printers, you will need to take the finished print off the print bed using a palette knife and then conduct some post-processing snipping off of extra plastic, as well as a bit of sanding. Removing the finished print is a bit more problematic for resin printers as much additional resin remains. In addition, We will clean your things with isopropyl alcohol and put them in the UV oven for final processing. Both printer types require post-processing; however, filament printers can be easier to operate.
Printing Speed
Draft Resin is a fast-printing SLA substance that can manufacture components up to 5-10X quicker than FDM 3D printers. With a 200-micron layer height, Draft Resin is precise enough to suit prototype demands while permitting faster design revisions. More giant sculptures that take up most of the building capacity of an SLA printer (about a 15 cm cube) require just roughly nine hours to produce with Draft Resin. Printing the identical object at 200-micron layers on an FDM printer can take 80-90 hours. This low time is great for prototyping with users because it allows them to try out different designs quickly. They can move on to another print or project.
SLA printing is faster than FDM when printing parts of comparable size at similar layer heights with various materials. But a part produced on an FDM printer with 100-micron layers will look much different from a part made with 100-micron layers on an SLA printer because of how each technology forms the layers. Achieving equal quality with FDM products will require lower layers height —thus two to four times longer printing time— or considerable and time-consuming post-processing to improve surface smoothness.
Build Volume
One area where FDM printers historically dominated used to be build volume. Due to technological changes, constructing more giant FDM machines is less challenging. There are various more extensive FDM options on the market for applications that demand 3D printing more significant pieces.
The inverted SLA method underpinning desktop SLA printers decreases footprint and cost, but increased peel pressures create constraints around materials and build volume. More significant pieces require substantial support structures to print appropriately.
Low Force Stereolithography
With the development of the Low Force Stereolithography (LFS) print method that powers, Formlabs has re-engineered resin-based 3D printing to substantially minimize the stresses placed on items during the print process. Uniform linear lighting and the low forces from the flexible tank imply Low Force Stereolithography technology can effortlessly grow up to a more significant print area built around the same strong print engine.
The first cheap large format resin printer, the Form 3L, creates huge components rapidly, employing two staggered light processing units (LPUs) that operate simultaneously along an optimal print path. Delivering a build volume five times greater than modern SLA printers, the Form 3L addresses size limits that can hamper processes on smaller desktop devices while retaining a reasonable pricing point.
Materials and applications
Some extrusion 3D printers work with a range of plastics and conventional thermoplastic filaments, such as ABS and PLA. The popularity of FDM 3D printing in the hobbyist arena has led to an excess of color possibilities. Various experimental plastic filaments mixtures also exist to build wood- or metal-like surfaces.
Certain FDM materials are available in engineering plastics, such as Nylon, PETG, PA, or TPU, and high-performance thermoplastics like PEEK or PEI; they are generally limited to chosen professional FDM printers that support them.
SLA resin materials offer the benefit of a wide range of formulation configurations. For example, they may be soft or hard, highly packed with additives like glass and ceramic, or endowed with mechanical qualities like high heat deflection temperature or impact resistance. Various resin formulas offer a wide variety of optical, mechanical, and thermal qualities to match conventional, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
In some circumstances, this mix of adaptability and utility leads organizations to adopt SLA 3D printing in-house initially. Once a printer can use one material, it is not long before printers can use the properties of many different materials. The more applications a material can perform, the more uses you can put it to in your 3D printing.
Printed Part Durability
Even when utilizing basic resins like PLA, parts produced from filament have a long lifespan. Additionally, you may use other materials such as PETG and ABS for exterior details, which provide enhanced strength and heat/UV resistance. When pressures operate across layers, components created with an FDM 3D printer significantly reduce strength. Hence it is vital to consider part orientation to optimum strength.
Standard resin prints are fragile and should not be used for functioning parts subjected to significant forces. Furthermore, because the resin is UV reactive, exposure to sunshine causes the prints to deteriorate. However, high-strength resins on the market can assist resin prints to be more durable. Unfortunately, we’ve discovered that this resin is difficult to remove from printed parts and frequently leaves a sticky residue on prints. We’ve had better luck combining this resin with standard resins to counteract the negative effects while increasing the strength.
Software Setup
Once assembled, learning the many parameters available for filament printers in the printer slicer software to obtain the most excellent quality prints might take some time. Although many current slicers, such as PrusaSlicer and Cura, provide prepared profiles for most Creality printers, it is still necessary to understand how the various settings function because tweaks are sometimes required to improve printing for certain types of models. To achieve the most significant results, you’ll need to experiment with how the models are orientated on the printer.
Resin printers have significantly fewer settings to configure, and once the printer is installed, it’s simple to start printing right away. The layer duration (how long each layer is exposed to UV light to cure) and material support parameters are the only settings you’ll ever need to adjust. Throughout resin printers, print orientation is also critical to ensure that the print remains stuck to the bed for the print duration. Overall, resin printers are easier to set up initially because of their basic setup and print settings.
Advantages of Resin and SLA 3D printing
SLA and resin 3D printers provide a slew of advantages. These include:
- 3D models that are highly accurate.
- a flawlessly finished exterior
- The wide diversity of material
- Cost-savings in manufacturing
- Large-volume
- Stiffness and strength
- Chemically impervious
- Prints with greater detail and clarity
Buying Guide for Resin 3D Printers
Choosing the appropriate 3D printer is a superior choice, so it’s crucial that you thoroughly explore your alternatives before buying. That also includes thinking about what is most essential to you in a 3D printer. With that in mind, here are some of the critical things to consider when buying your 3D printer.
Purpose of Use
When buying your 3D printer, you should consider using it for what. This idea might have a significant effect on the sort of equipment that you should be buying. we can make a range of useful or valuable objects with a 3D printer
First of all, you may construct the types of stuff you would commonly find about the house. If you intend on manufacturing home products with your 3D printer, you should acquire an FDM printer. If you will be building the objects, you use with food, coat them with a food-safe epoxy.
You may also create parts that you can utilize outside. In this instance, you are going to require something exceptionally sturdy. In this situation, you should use a material similar to ABS. To that end, resin printers are the way to go if you’re printing art on your 3D printer. You can use a resin printer may be used to create professional-quality goods. To produce heavy-duty equipment, you may have to spend a bit more money on your 3D printer.
Think about what you want to do with the 3D printer in the long run. Is it something you merely wish to dabble with and use for pleasure, or do you intend on utilizing it in the long term for more extensive projects? There’s no use in getting a cheap 3D printer that will only provide you a primary degree of capability if you have more significant projects planned further down the line. If you want to use your 3D printer for more than just entertainment, it’s a good idea to invest in one that provides the extra functionality that you need.
Style of the Printer
Many printer models on the market may be worth considering. Again, what you pick can impact the types of things you can manufacture with the printer. The earliest type of 3D printer is the FDM printer. These are tools that people who like to do 3D printing as a hobby use. It’s frequently advisable to choose a Cartesian type structure of FDM as this usually will provide you substantially greater control, and it may also boost the outcomes that you obtain in the end.
For very intricate work, you should choose an SLA printer. These printers are highly accurate. On the other hand, DLP printers are significantly smoother in terms of operation than FDM machines are. You may also go for SLS or Selective Laser Sintering printers, although they are generally suitable for making industrial-level items that may be a bit harder to produce.
If you are looking for a beginner’s 3D printer, it’s probably better to acquire an FDM printer, and they are typically a lot more economical.
Quality
It’s crucial to check the overall quality of the printer before you buy. The two most important aspects of a printer are its print speed and the quality of its printing resolution.
When you need to get a lot of detail in your projects, you should use a printer with lower microns. Besides this, if the printer can move its extruder faster, it will print the goods much more quickly. Additionally, if the printer can extrude plastic more quickly, it will produce its products much more rapidly.
It can often be a bit difficult to assess the quality of the printer merely by reading the specs provided forth by the manufacturer, though. In these cases, it’s wise to resort to the internet for guidance! Other customers will often share images of their completed results, and these may demonstrate to you the quality of output you’re getting from the printer.
Safety Functions
3D printing can get reasonably hazardous if you’re not careful, so it’s crucial to ensure that your machine has specific measures in place in case something goes wrong. There are various safety features in particular that you should consider acquiring. For instance, search for models that include automated nozzle cooling once you have completed printing. Sometimes 3D printers will come with heated beds, and the printer may come with an automatic shut-off mechanism when the project is complete. These are just a few things that you should take into account.
Function of Printing Resume
Unexpected events may occur from time to time. For example, your printer may unexpectedly halt in the middle of a job, maybe due to a power outage. Naturally, you do not want to have your entire printing endeavor wrecked. A print resume function can be pretty helpful in these instances. Rather than starting the job initially, your printer will pick up where it left off.
user experience
Having an easy-to-use 3D printer may go a long way toward making your user experience significantly more pleasurable. After all, you don’t want to waste too much time fiddling with a rotary knob. With this in mind, you should try to get a printer with a touchscreen interface if at all feasible, as they are often easier to operate.
Print Bed Size
The size of your 3D printer’s print bed can affect the size of projects you can create, so it’s vital to consider this thoroughly. If the print bed is more significant, you will print more large parts. However, if you’re mostly building smaller items, this may not be as crucial to you.
Mono or RGB LCD
The masking LCD on your resin 3D printer can have the most significant impact on print speed. RGB masking LCDs are less expensive because we extensively used them in other devices, but they are slower because they do not allow UV light to pass through efficiently and require more exposure time per layer. The RGB LCD on the Creality LD-002R, for example, takes 9 seconds per layer, whereas the Mono LCD on the Elegoo Mars 2 Pro takes only 2.2 seconds.
How much build volume do you require?
Because most resin 3D printers have smaller build volumes than FDM 3D printers, you may discover that this limits you. If you wish to print massive pieces, a large format resin 3D printer like the Elegoo Saturn or the Anycubic Photon Mono X is a good option.
2K, 4K, or Beyond?
The Elegoo Mars 2 Pro, a resin 3D printer with a 6.08-inch 2K screen, can achieve an XY resolution of.05mm and a layer height of.05mm. For context, this means that even a low-resolution resin 3D printer can produce exceedingly tiny details that would be impossible to achieve with an FDM printer. A 4K screen can provide finer details if you require even higher resolution, but it is often more expensive.
What is Post-Processing Equipment?
Resin 3D printers produce pieces that need to be post-processed before being used. Typically, this workflow entails rinsing the parts in a solvent to remove any excess resin on the component’s surface, then curing the part using UV radiation to polymerize it fully. This process can be done manually by immersing the item in a solvent and fixing it with a low-cost UV laser. Still, some manufacturers have developed post-processing equipment, such as the Elegoo Mercury X, that automates the process and minimizes the mess.
Additional Features
So, what more does your 3D printer have to offer? There are a few things to keep an eye out for. First and foremost, how is the printer’s connectivity? Is it simple to connect to a computer or laptop, or does it require a unique device, such as an SD card, to function? Also, does the printer come fully completed, or will you be purchasing a 3D printer kit? Finally, think about how much noise the 3D printer creates. These machines can be rather loud, so it’s worth thinking about whether you’ll be working in a setting where noise is an issue. If that’s the case, you might want to look into obtaining a quieter model.
FAQ
Instead of using a solid plastic, melting it into a shape, and then letting it solidify again, resin 3D printing uses a liquid resin held in a tiny VAT and curing the desired shape with a flash of UV light (which hardens the resin). The build plate on the resin printer then goes higher, and the procedure is repeated, gradually building up your object.
Stereolithography is part of the vat photopolymerization family of additive manufacturing processes, sometimes known as resin 3D printing. These devices work by curing liquid resin with light from a laser or projector. The primary physical differences are in the layout of the light source, construction platform, and resin tank. SLA resins are subjected to various wavelengths of light to polymerize monomers and oligomers into rigid or flexible shapes.
It all depends on what you want to publish. It’s entirely fair to have a resin and filament FDM printer, and many people do. Resin printers are far superior if you wish to print small complex models – perhaps miniatures for printing – or other complicated pieces like jewelry. Unless you’re willing to spend a lot of money on a resin printer, you’ll be limited to creating far smaller products than you could with even the most basic filament 3D printer. Resin is more expensive and challenging to print with, but the results may be breathtaking.
Refrence
- tomshardware.com
- formlabs.com
- cdw.com
- pcguide.com
- crealityexperts.com