A rapidly expanding sector, 3D printing has a wide range of uses, from medical research to aeronautical engineering. The techniques and materials utilized for 3D printing also change as technology advances. 3D Printer Glue Stick is one such item that has grown in popularity recently.
Glue sticks are a quick and inexpensive substitute for common 3D printing adhesives like hairspray and glue sprays. They are simple to use, offer good adhesion, and work with a variety of 3D printing materials. Printing errors can result from using the incorrect type of glue stick or applying them improperly. Unfortunately, not all glue sticks are created equal.
We’ll give you a thorough explanation of how to use glue sticks for 3D printing in this post. In this blog post, We’ll cover all aspects, including different glue stick types. We’ll also explore advanced techniques for optimal adhesion. We will also go through typical issues that occur while using glue sticks and how to fix them. By the end of this post, you’ll gain essential knowledge for 3D printing with glue sticks. You’ll be equipped with the skills needed to achieve success in your projects.
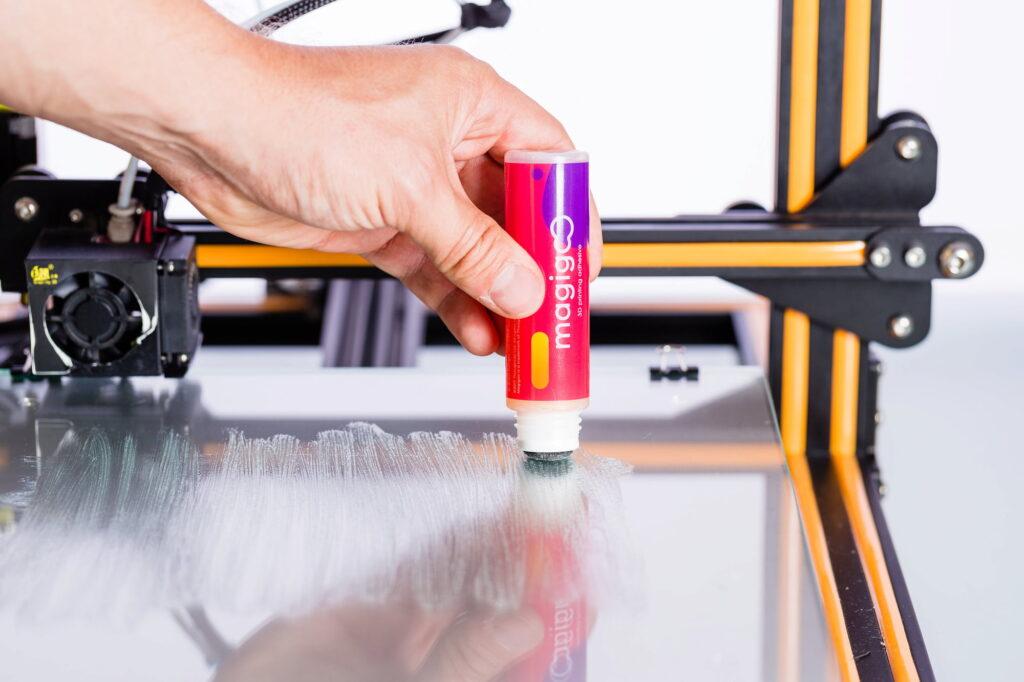

Introduction to 3D Printer Glue Stick
We will expose you to the fundamentals of 3D printing with glue sticks in this section. We’ll start by defining glue sticks and describing how they work. The make-up glue sticks activate when a combination of polymers and adhesives heats them. The substance being printed forms a solid binding with the surface when you apply it.
Importance of adhesion in 3D printing
Adhesion is crucial for 3D printing success, impacting quality, accuracy, and appearance. The first layer forms the print’s foundation, sticking to the build plate effectively. Proper adhesion ensures the accurate placement of subsequent layers, creating a stable product. Poor adhesion can lead to distortion, curling, or separation from the build plate. Inadequate adhesion may jeopardize the entire 3D printing project. Finding efficient adhesion solutions is crucial for 3D printing enthusiasts to ensure the best outcomes. This problem can result in not only material loss but also frustration and lost time.
Introduce 3D printer glue stick as an adhesion solution
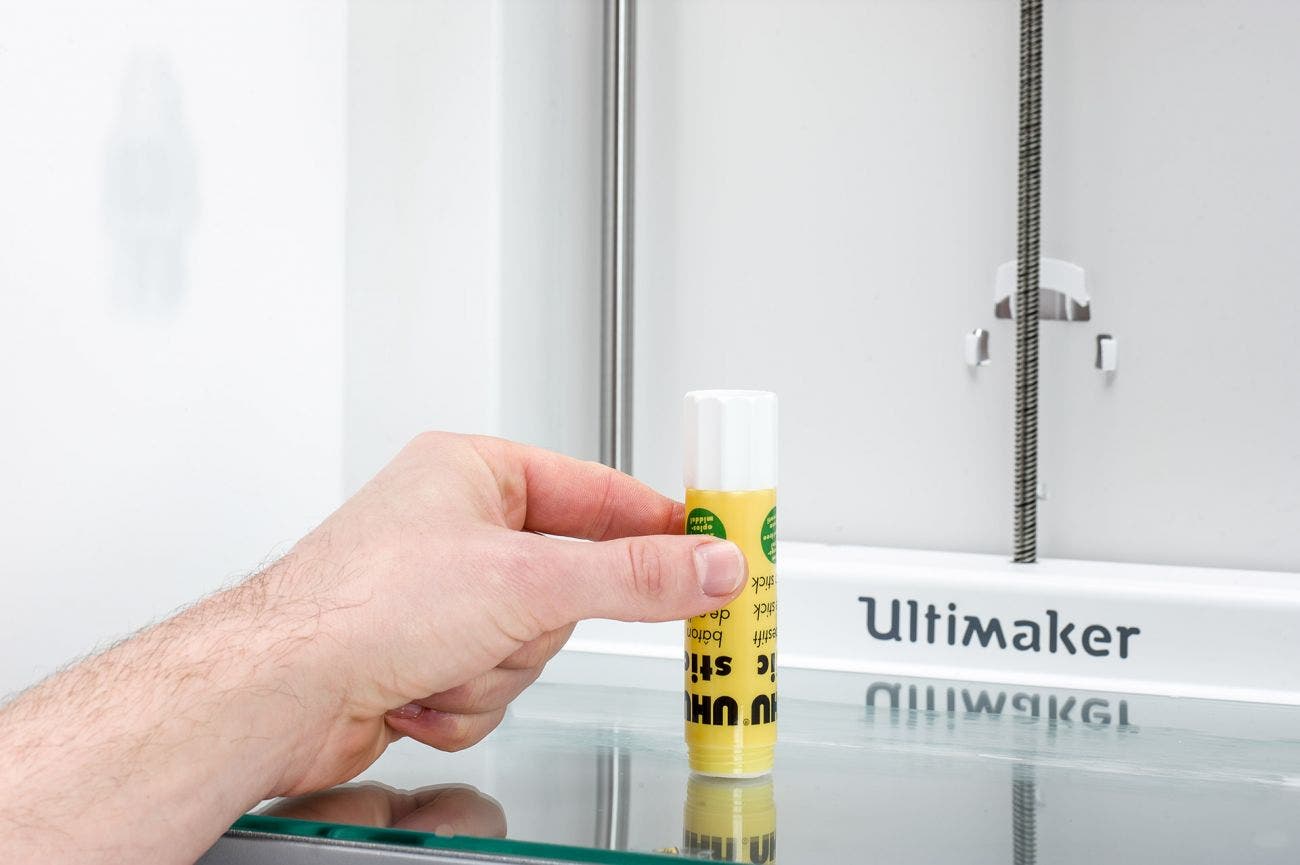
The 3D printer glue stick has become a well-liked and effective adhesion solution for a variety of 3D printing applications. The simple tool aims to temporarily link the first print layer and build a plate for a solid foundation. It’s ideal for both new and experienced 3D printing enthusiasts due to its ease of use. The low cost and compatibility with various print materials make it a perfect option. The 3D printer glue stick has become a vital part of achieving ideal print quality. It reduces adhesion-related issues, making it a reliable and affordable solution.
The Adhesion Challenge in 3D Printing
The adhesion challenge in 3D printing involves ensuring the first layer sticks to the build plate. This layer is crucial as it serves as a foundation for subsequent layers. Improper adhesion can cause warping, curling, or detachment of the print. These issues lead to poor quality, wasted materials, and lost time. 3D printing enthusiasts prioritize finding effective adhesion solutions. 3D printer glue sticks are more universally effective than other methods. Alternative methods include specialized build plates, adhesive tapes, or sprays.
Importance of first-layer adhesion
In 3D printing, the first-layer adhesion holds immense significance, as it establishes the foundation for the complete printing procedure. A strong first-layer bond is crucial for structural integrity and overall quality. Proper first-layer adherence ensures precise placement of subsequent layers. This prevents shifting or misalignment during printing. Good adhesion minimizes warping and curling risks. These issues arise when materials cool and contract unevenly. Optimal first-layer adhesion is vital for successful 3D printing projects. It helps avoid wasted time, materials, and frustration.
Consequences of poor adhesion
Poor adhesion in 3D printing often leads to failed prints, wasted resources, and user frustration. Improper first-layer adhesion can cause warping, with print edges lifting off the build plate. It can also result in curling, where print corners begin to bend. These problems may affect the finished product’s overall aesthetic, dimensional accuracy, and structural integrity. Poor adhesion can sometimes cause prints to entirely separate from the build plate, wasting materials and causing hours of downtime. In extreme circumstances, prints that come loose while printing can even harm the printer. Ultimately, addressing adhesion issues is crucial for successful 3D printing projects. This ensures printer efficiency and longevity, maintaining optimal performance.
Traditional adhesion solutions and their drawbacks
Poor first-layer adhesion is a challenge for 3D printing. Traditional adhesion methods have their drawbacks. Customized build plates or coatings can be effective but costly. Adhesive tapes like blue painter’s tape can improve adhesion. However, they wear out quickly and need frequent replacement. Adhesive or hair sprays are an option but can be messy and leave a residue. Conventional solutions may not work equally well with all materials or printer configurations. User experimentation is necessary to determine the best adhesion technique for specific requirements. 3D printer glue sticks offer a more adaptable, affordable, and user-friendly adhesive solution. Glue sticks are suitable for a variety of 3D printing applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printer Glue Stick
Advantages of 3D Printer Glue Stick
- Easy to apply: Using a glue stick is a simple process, making it user-friendly for beginners and experienced users alike.
- Cost-effective: Compared to alternatives like specialized build plates, adhesive tapes, or sprays, glue sticks provide an affordable adhesion solution.
- Compatibility: The glue stick works with different print materials, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and more. It’s versatile for various 3D printing applications
- Easy removal: Cleaning glue stick residue off the build plate is easy. Use water to clean the plate. This ensures a clean surface for your next print.
- Widely available: Most users can access 3D printer glue sticks, which are available at most office supply stores and online.
- Temporary adhesion: Glue sticks create a temporary bond that anyone can easily break once they complete the print. This reduces the risk of damaging the print while removing it.
Disadvantages of 3D Printer Glue Stick
- Not suitable for all build surfaces: Glue sticks may not be compatible with all build surfaces or coatings. This may require the use of alternative adhesion methods. Specialized build surfaces or coatings can be expensive and difficult to maintain. Adhesive tapes can wear out quickly and need to be replaced frequently. Adhesive sprays or hair sprays can leave residue on the build plate. Heated build plates may not be suitable for all types of filaments. Finding the best adhesion solution depends on individual needs and preferences.
- Potential for uneven application: Applying an uneven layer of glue can lead to poor adhesion, warping, or print failure.
- Requires reapplication: The 3D printing process requires that you reapply glue sticks before each print, which adds an extra step.
- Storage concerns: Store glue sticks properly to prevent them from drying out and becoming unusable. Keep them in a cool, dry place, and make sure the cap is on. Proper storage helps to maintain the effectiveness of the glue sticks. Glue sticks can lose their adhesion properties if exposed to air or high humidity. Storing them correctly ensures that they remain usable for longer.
- Inconsistent performance: Some brands of glue sticks may not work as well as others, and performance may vary depending on filament type or build plate material, requiring experimentation to find the best fit.
- Environmental impact: The frequent use and disposal of glue sticks may contribute to plastic waste and environmental concerns.
Types of 3D Printer Glue Stick
In this section, we will discuss the different types of glue sticks that are suitable for 3D printing. There are several types of glue sticks available, and not all of them are suitable for 3D printing.
The most commonly used glue sticks for 3D printing are the standard white or clear glue sticks, which are widely available and affordable. These glue sticks are suitable for most 3D printing materials, including PLA, ABS, and PETG.
Manufacturers design purple glue sticks specifically for use with PLA, a material that can be difficult to adhere to some surfaces. You can use these glue sticks for 3D printing, as they are another type. The glue stick’s purple color shows where the user has applied it and helps to ensure even coverage.
The manufacturers formulate some glue sticks specifically for 3D printing materials like wood or flexible filaments. These glue sticks may contain different additives that provide better adhesion for those materials.
Please note that you should be aware that some glue sticks may work better for 3D printing than others since they are not all created equal. When choosing a glue stick for 3D printing, it is important to consider factors such as adhesion strength, compatibility with your 3D printing material, and ease of application.
How to Apply Glue Sticks to 3D Printing Surfaces
In this section, we will discuss the best practices for applying glue sticks to 3D printing surfaces. Proper application is crucial for achieving optimal adhesion and preventing printing failures.
Before applying the glue stick, it is important to clean the 3D printing surface thoroughly to remove any dust or debris. You can do this by using a damp cloth or a specialized cleaning solution.
Next, the glue stick should be applied in a thin, even layer across the entire printing surface. It is important to avoid applying too much glue, as excess glue can build up and interfere with the printing process.
After applying the glue stick, the printing surface should be allowed to dry completely before beginning the printing process. This usually takes only a few minutes.
Tips for Getting the Best Adhesion with 3D Printer Glue Stick
In this section, we will provide you with some tips for achieving the best adhesion when using glue sticks for 3D printing. These tips can help you avoid printing failures and produce high-quality prints.
One of the most important factors for achieving good adhesion is to use the right type of glue stick for your 3D printing material. Different materials may require different types of glue sticks or different application methods.
It is also important to ensure that the glue stick is applied in a thin, even layer. Too much glue can cause problems such as oozing or blobbing, while too little glue may not provide enough adhesion.
In addition, it is important to pay attention to the temperature of the printing surface. If the surface is too hot or too cold, it can affect the adhesion of the glue stick. It is recommended to keep the printing surface at a temperature of around 60-70°C for optimal adhesion.
Common Problems and Solutions When Using 3D Printer Glue Stick
In this section, we will discuss some common problems that can arise when using glue sticks for 3D printing, as well as some solutions to those problems.
One of the most common problems is printing failures due to poor adhesion. This can be caused by using the wrong type of glue stick, applying the glue stick incorrectly, or not allowing it to dry completely before beginning the printing process. To solve this problem, it may be necessary to experiment with different types of glue sticks or adjust your application technique.
are some precautions that should be taken to avoid potential hazards.
Firstly, it is important to use glue sticks in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any fumes that may be released during the printing process.
It is also important to avoid direct skin contact with the glue stick or the printing surface, as the hot glue can cause burns.
Finally, it is important to store glue sticks in a cool, dry place away from heat sources or open flames.
Troubleshooting Glue Stick Issues in 3D Printing
In this section, we will discuss some common 3D Printer Glue Stick issues that can arise during the 3D printing process and how to troubleshoot them.
One issue is inadequate adhesion, which can be caused by using the wrong type of glue stick or not applying it correctly. To solve this problem, it may be necessary to experiment with different types of glue sticks or adjust your application technique.
Another issue is excess glue buildup on the printing surface, which can interfere with the printing process. To solve this problem, it is important to apply the glue stick in a thin, even layer and to clean the printing surface regularly to remove any excess glue.
Alternative Adhesion Solutions
Alternative adhesion solutions in 3D printing offer various options for users to improve first-layer adhesion, depending on their specific requirements, materials, and printer setups. BuildTak or PEI sheets are popular choices as they provide a durable and reusable surface that promotes strong adhesion for different types of filaments. Blue painter’s tape is another option that is easy to apply and remove but may require frequent replacement due to wear and tear.
Hair spray or specialized adhesive sprays can also improve adhesion, although they may be messy and necessitate proper ventilation due to their fumes. Heated build plates are particularly useful for materials like ABS, which tend to contract and warp when cooling; however, they may not be suitable for all types of filaments and may require additional energy consumption. Ultimately, finding the best adhesion solution depends on the individual needs and preferences of the user, as well as the specific materials and printer setup they are working with.
BuildTak or PEI sheets
In the field of 3D printing, BuildTak and PEI (Polyetherimide) sheets are well-liked adhesion solutions because they provide a robust, reusable, and adaptable surface for a variety of materials. Both methods offer great first-layer adhesion, which is necessary for producing prints of high quality. BuildTak is a thin, flexible sheet that sticks to the build plate, creating a surface that encourages strong adhesion without the need for additional treatments.
PEI sheets, on the other hand, are made of a thermoplastic polymer and may be fastened to the build plate using binder clips or adhesive backing. Because of their well-known high-temperature resistance, they can be used with both heated and unheated construction plates. Although BuildTak and PEI sheets both provide better stickiness and are reasonably simple to use, they can be more expensive than alternative adhesion options like glue sticks or painter’s tape. Depending on how frequently and how intensely they are used, they can also need occasional maintenance or replacement.
Blue painter’s tape
Blue painter’s tape is a widely-used adhesion solution in 3D printing, particularly for those working with PLA filaments. This easy-to-apply, removable tape provides a textured surface that promotes adhesion between the first layer of the print and the build plate. One of the main advantages of using blue painter’s tape is its accessibility, as it can be found in most hardware stores at an affordable price. To use it, users simply need to apply strips of tape onto the build plate, ensuring a smooth, even surface without any gaps or overlaps.
While blue painter’s tape is a cost-effective solution, it does have some drawbacks. It tends to wear out quickly, requiring frequent replacement to maintain optimal adhesion. Moreover, it may not be the most effective solution for all types of filaments, particularly those that require higher printing temperatures, such as ABS or PETG. In such cases, alternative adhesion solutions like heated build plates, PEI sheets, or glue sticks may be more suitable.
Hair spray or adhesive sprays
Hair spray or adhesive sprays are another option for improving first-layer adhesion in 3D printing. These sprays create a thin, tacky film on the build plate, providing a surface that encourages the print material to stick during the printing process. Many users find success with hair sprays, which are readily available and affordable, while others prefer specialized adhesive sprays designed explicitly for 3D printing. To use these sprays, users need to apply a light, even coat on the build plate, allowing it to dry before starting the print.
Despite their effectiveness in promoting adhesion, hair spray and adhesive sprays have some drawbacks. They can be messy to use and may leave residue on the build plate that requires thorough cleaning. The chemicals used in these sprays can also emit fumes, making proper ventilation a necessity when applying them. Additionally, these sprays may not be compatible with all types of filaments or build plate materials, so it’s essential for users to test their compatibility before use. In cases where hair spray or adhesive sprays may not be the ideal solution, users can explore other adhesion methods such as glue sticks, blue painter’s tape, or specialized build surfaces like PEI sheets and BuildTak.
Heated build plates
Heated build plates have become an increasingly popular adhesion solution in 3D printing, particularly for materials that are prone to warping or have higher printing temperature requirements. By raising the temperature of the build plate, heated build plates reduce the thermal stress that occurs when the printed material cools down and contracts, minimizing the risk of warping or curling. This method is especially effective for filaments like ABS, which are notorious for their tendency to contract and warp during the cooling process.
While heated build plates can significantly improve adhesion and print quality, they also have some drawbacks. Firstly, they consume more energy, which may result in increased operational costs. Additionally, not all printers come equipped with heated build plates, and upgrading to one may require a considerable investment. It is also worth noting that heated build plates may not be the best solution for all types of filaments, as some materials like PLA might not require additional heat for proper adhesion. In situations where heated build plates are not an ideal solution, users can explore alternative adhesion methods, such as glue sticks, blue painter’s tape, or adhesive sprays, to find the most suitable option for their specific needs and materials.
Future of 3D Printer Glue Stick
While the market for practical and user-friendly adhesion solutions in additive manufacturing keeps expanding, the future of 3D printer glue sticks seems bright. The demand for dependable and adaptable adhesion products like glue sticks will continue to be high as 3D printing technology develops and becomes more affordable for enthusiasts, educators, and professionals alike.
It is anticipated that formulas for glue sticks made exclusively for 3D printing applications would become more inventive. These novel formulas might provide enhanced functionality, compatibility with a wider variety of materials, and even greater usability. Also, the development of environmentally friendly glue sticks comprised of biodegradable or sustainable materials may aid in resolving environmental issues related to the disposal of conventional glue sticks.
The best practices for employing glue sticks will spread as the 3D printing community continues to exchange information and experiences, further strengthening their position in the toolkit. Also, partnerships between producers of glue sticks and providers of 3D printers may result in the creation of fresh goods that are tailored to function flawlessly with particular printer types or materials.
In conclusion, the future of 3D printer glue sticks appears promising because they are likely to continue to be a crucial tool for getting the best possible adhesion and print quality in the constantly changing field of 3D printing.
Conclusion: Achieving Success with 3D Printer Glue Stick
In this final section, we will summarize the key points covered in the book and emphasize the importance of proper glue stick usage for achieving success in 3D printing. With the knowledge and techniques presented in this book, readers should be well-equipped to achieve high-quality prints with glue sticks as their adhesive of choice.
In conclusion, glue sticks offer a simple and affordable solution for 3D printing adhesion, and are compatible with a wide range of materials. However, proper application and maintenance are crucial for achieving optimal adhesion and avoiding printing failures.
By following the best practices outlined in this post, readers can confidently use glue sticks for their 3D printing projects and achieve successful results. From cleaning and maintaining the printing surface to experimenting with different application techniques and types of glue sticks, there are many strategies for achieving the best possible adhesion.
As the field of 3D printing continues to evolve, new adhesives and techniques will likely be developed. However, glue sticks will likely remain a popular and effective option for many 3D printing applications.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced 3D printing enthusiast, this post provides valuable information and insights into the use of glue sticks for 3D printing. We hope that you find it informative and helpful, and wish you success in your future 3D printing endeavors.
How to Use a 3D Printer Glue Stick?
Time needed: 30 minutes
These steps provide a straightforward guide to using a 3D printer glue stick to achieve optimal adhesion and print quality. By following this process, users can benefit from the simplicity and effectiveness of glue sticks as an adhesion solution for their 3D printing projects.
- Clean the build plate
Remove any dust, debris, or residue from the build plate to ensure proper adhesion and prevent contamination of the glue stick.
- Heat the build plate (optional)
If your printer has a heated build plate, preheat it to the recommended temperature for the specific material you are using. This helps the glue stick to spread evenly and enhances adhesion.
- Apply the glue stick
Gently apply a thin, even layer of glue to the build plate, covering the entire area where the first layer of your print will be deposited. Ensure that the layer is consistent, avoiding any clumps or gaps.
- Start your print
With the glue stick applied and the build plate prepared, start your 3D print, ensuring that the first layer adheres properly to the glue-covered surface. Monitor the initial adhesion to make any necessary adjustments to the print settings or glue application.
- Remove the print and clean the build plate
After the print is complete and has cooled down, carefully remove it from the build plate. Clean the build plate thoroughly to remove any remaining glue residue before starting your next print.
FAQs
Although regular glue sticks can sometimes work for 3D printing adhesion, it’s best to use a glue stick specifically designed for 3D printing applications. These glue sticks are formulated to provide better adhesion and compatibility with various print materials.
It’s recommended to reapply the glue stick whenever you notice that the adhesion is not as strong as it should be, or when you clean the build plate. The frequency of reapplication depends on the number of prints and the material used.
Yes, you can use a 3D printer glue stick with a heated build plate. Applying the glue stick to a heated build plate can help the glue spread more evenly and improve adhesion for materials that require higher printing temperatures.
3D printer glue sticks are generally compatible with a wide range of filaments, such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and others. However, it’s always best to check the manufacturer’s recommendations for your specific glue stick and filament to ensure compatibility.